Slow-wave sleep is a stage of sleep that is characterized by low-frequency, high-amplitude brain waves called delta waves.
Slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, is crucial for the body to repair and rejuvenate itself. During slow-wave sleep, the body’s muscles relax, heart rate and breathing slow down, and blood pressure drops.
Slow-wave sleep is one of the four stages of sleep, with the other three being rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and two other non-REM stages. Slow-wave sleep typically occurs during the first half of the night, and the amount of time spent in this stage decreases as the night progresses. It is most commonly associated with N3, the third stage of non-REM sleep.
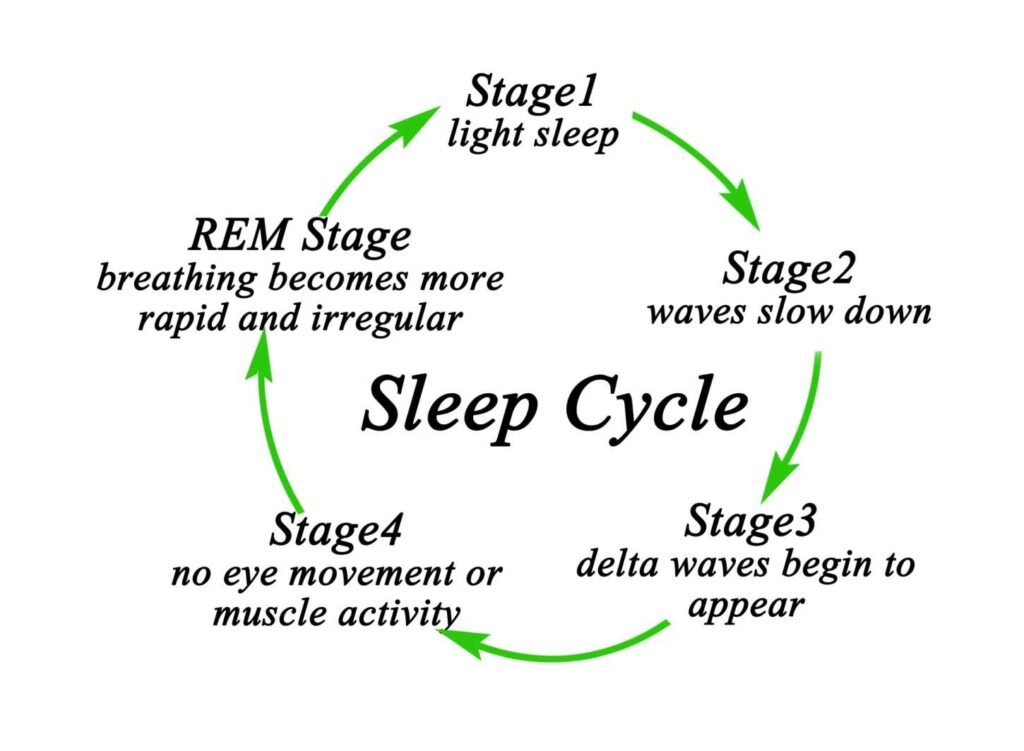
The quality of slow-wave sleep is an important factor in overall sleep quality. Individuals who do not get enough slow-wave sleep may experience a range of negative health effects, including fatigue, decreased cognitive function, and an increased risk of developing certain health conditions. Understanding the importance of slow-wave sleep and how to improve its quality can help individuals achieve better overall health and well-being.
Physiology of Slow-Wave Sleep
Slow-wave sleep (SWS) is a phase of sleep that is characterized by low-frequency, high-amplitude brain waves known as delta waves. During SWS, the brain undergoes a series of physiological changes that are essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of the body.
Brain Activity and Delta Waves
Delta waves are generated by the thalamus and cortex of the brain during SWS. These waves are believed to reflect the synchronization of neural activity between different regions of the brain. The slow oscillation of delta waves is thought to be important for consolidating memories and facilitating learning.
The Role of Slow-Wave Sleep in Growth and Repair
SWS is critical for the growth and repair of tissues and organs in the body. During SWS, the body releases human growth hormone (HGH), which is essential for tissue repair and growth. HGH stimulates the production of new cells and tissues, and it also helps to regulate the immune system.
In addition to HGH, SWS is also important for the regulation of energy metabolism. During SWS, the body undergoes a process known as glymphatic clearance, which allows the brain to remove waste products and toxins. This process is critical for maintaining the health of the brain and preventing neurodegenerative diseases.
Overall, SWS plays a crucial role in the maintenance of physical and mental health. By facilitating growth, repair, and maintenance of the body, SWS ensures that individuals are able to function at their best.
Impact on Health and Disorders
Memory Consolidation and Cognitive Function
Slow-wave sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and cognitive function. During this stage, the brain processes and consolidates new memories, allowing them to be stored and retrieved later. Research has shown that sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on memory consolidation and cognitive function, leading to decreased performance on tasks that require attention, concentration, and learning.
Sleep Disorders and Disturbances
Sleep disorders and disturbances can have a significant impact on slow-wave sleep. Insomnia, sleep apnea, sleepwalking, and night terrors are just a few examples of sleep disorders that can disrupt slow-wave sleep, leading to decreased memory consolidation and cognitive function. Parasomnias, which are abnormal behaviors that occur during sleep, can also disrupt slow-wave sleep and lead to decreased cognitive function.
Influence of Lifestyle and Aging
Lifestyle factors such as exercise, alcohol consumption, caffeine intake, and shift work can all have an impact on slow-wave sleep. Exercise has been shown to improve slow-wave sleep, while alcohol and caffeine can disrupt it. Shift work can also disrupt sleep patterns, leading to decreased slow-wave sleep and increased risk of sleep disorders.
Aging is another factor that can impact slow-wave sleep. As people age, the amount of time spent in slow-wave sleep decreases, leading to decreased memory consolidation and cognitive function. However, research has shown that exercise and good sleep hygiene can help improve slow-wave sleep in older adults.
In conclusion, slow-wave sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and cognitive function. Sleep disorders, lifestyle factors, and aging can all have an impact on slow-wave sleep, leading to decreased cognitive function and increased risk of sleep disorders. It is important to maintain good sleep hygiene and address any sleep disturbances to ensure adequate slow-wave sleep and overall health.
Understanding Circadian Rhythm: The Body’s Natural Clock Explained

Circadian rhythms are physical, mental, and behavioral changes that follow a roughly 24-hour cycle, responding primarily to light and darkness in an organism’s environment. These rhythms are driven by an internal biological clock, which is known as the circadian clock or the biological clock.
Continue reading: Understanding Circadian Rhythm
MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin Review: Do They Work?

These gummies are designed to promote relaxation and support sleep quality for adults. Unlike many other sleep aids, they don’t contain melatonin, so you won’t wake up feeling groggy or drowsy.
Continue reading: MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin





