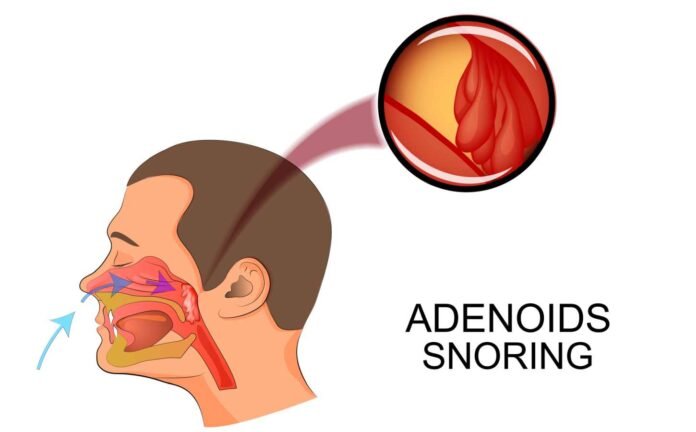
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the adenoids, which are small lumps of tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity.
The adenoids are part of the immune system and help to fight off infections, but they can sometimes become enlarged and cause problems with breathing, sleeping, and hearing. Adenoidectomy is commonly performed on children, but adults may also undergo the procedure in certain cases.
The most common reason for adenoidectomy is to treat chronic or recurrent infections of the adenoids, such as tonsillitis or sinusitis. Enlarged adenoids can also cause nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, snoring, and sleep apnea. In some cases, adenoidectomy may be recommended to improve the effectiveness of other treatments, such as allergy medications or continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy for sleep apnea. Despite its benefits, adenoidectomy is not without risks, and patients should discuss the potential complications and benefits with their healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure.
Understanding Adenoidectomy
What Are Adenoids?
Adenoids are small glands located at the back of the nose, just above the tonsils. They are part of the immune system and help to fight off infections that enter the body through the nose. Adenoids are most active during childhood and tend to shrink in size as a person grows older.
Indications for Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the adenoids. This procedure is typically recommended when a person experiences recurrent infections or breathing problems due to enlarged adenoids. Some of the common indications for adenoidectomy include:
- Chronic or recurrent ear infections
- Chronic or recurrent sinus infections
- Breathing problems, such as snoring or sleep apnea
- Chronic or recurrent sore throats
- Enlarged adenoids that cause nasal congestion or difficulty breathing
Adenoidectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia and involves the use of a small instrument to remove the adenoids. The procedure is considered safe and effective, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in their symptoms after surgery.
In summary, adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the adenoids. It is typically recommended for individuals who experience recurrent infections or breathing problems due to enlarged adenoids. The procedure is considered safe and effective, and most patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms after surgery.
Pre-Operative Considerations
Assessment and Diagnosis
Before undergoing an adenoidectomy, a healthcare provider will assess and diagnose the patient’s condition. Children are more likely to require an adenoid removal surgery than adults. Symptoms such as difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, and sleep apnea may indicate the need for an adenoidectomy.
A healthcare provider may also order an X-ray or blood test to confirm the diagnosis. If the adenoids are inflamed or enlarged, surgery may be recommended.
Preparing for Surgery
Prior to surgery, patients should inform their healthcare provider of any medications they are taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements. They may need to temporarily stop taking certain medications to reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery.
Patients should also avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the surgery, as directed by their healthcare provider. They may need to arrange for transportation to and from the surgical facility, as well as arrange for someone to stay with them for the first 24 hours after surgery.
In summary, before undergoing an adenoidectomy, a healthcare provider will assess and diagnose the patient’s condition, and may order an X-ray or blood test. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of any medications they are taking and follow instructions regarding fasting and transportation.
The Adenoidectomy Procedure
Surgical Techniques
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed by an otolaryngologist to remove the adenoids, which are small glands located at the back of the nasal cavity. The procedure can be performed using various techniques, including:
- Curette technique: In this technique, the adenoids are removed using a curette, which is a spoon-shaped instrument. The otolaryngologist inserts the curette through the mouth and scrapes the adenoids away from the back of the nasal cavity.
- Cauterizing technique: In this technique, the otolaryngologist uses a cautery device, which emits electricity or radiofrequency energy, to remove the adenoids. The device burns and cauterizes the adenoid tissue, which is then removed.
- Microdebrider technique: In this technique, the otolaryngologist uses a microdebrider, which is a small, rotating instrument with a blade, to remove the adenoids. The microdebrider cuts and suctions the adenoid tissue, which is then removed.
Anesthesia and IV Administration
Adenoidectomy is performed under general anesthesia, which means the patient is unconscious during the procedure. The anesthesia is administered through an IV, which is a small tube inserted into a vein in the patient’s arm. The anesthesia medication is delivered through the IV, which allows the patient to remain asleep and pain-free throughout the procedure.
In conclusion, adenoidectomy is a common surgical procedure used to remove the adenoids. The procedure is performed by an otolaryngologist and can be done using various techniques, including the curette, cautery, and microdebrider. Adenoidectomy is performed under general anesthesia, which is administered through an IV.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Immediate Aftercare
After an adenoidectomy, the patient will be taken to a recovery room where they will be monitored by medical staff for a period of time. It is common for patients to experience some pain and discomfort immediately after the surgery. The medical staff will provide pain relief medication to help manage the discomfort.
Swelling is also common after an adenoidectomy. Patients may experience swelling in the throat and neck area. To help reduce swelling, ice packs may be applied to the neck area. The medical staff will monitor the patient’s swelling and provide additional treatment if necessary.
Recovery at Home
Once the patient is discharged from the hospital, they will need to continue with their recovery at home. It is important for the patient to rest and avoid any strenuous activities for a period of time. The length of time required for recovery will vary depending on the patient’s age and overall health.
Diet is an important consideration during the recovery period. Patients should avoid hard, crunchy, or spicy foods for a period of time. Soft foods such as ice cream or soup may be easier to swallow and can help soothe the throat.
Hydration is also important during the recovery period. Patients should drink plenty of fluids to help keep the throat moist and reduce the risk of dehydration.
Pain relief medication may be prescribed to help manage any pain or discomfort during the recovery period. It is important for patients to follow the medication instructions carefully and not exceed the recommended dosage.
In summary, post-operative care and recovery after an adenoidectomy is important for a successful outcome. Patients should follow all instructions provided by medical staff and take care to rest and avoid strenuous activities. Proper diet, hydration, and pain management are also important considerations during the recovery period.
Potential Complications and Risks
Common Complications
As with any surgical procedure, adenoidectomy carries some risks. The most common complications associated with adenoidectomy include bleeding, infection, and anesthesia-related complications.
Bleeding
Bleeding is a common complication of adenoidectomy. Although most cases of bleeding are minor and stop on their own, in rare cases, heavy bleeding may require a blood transfusion or a return to the operating room. Patients who experience bleeding after the procedure should contact their healthcare provider immediately.
Infection
Infection is another common complication associated with adenoidectomy. Patients may experience symptoms such as fever, pain, and swelling. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed to treat the infection.
Anesthesia
Adenoidectomy is performed under general anesthesia, which carries its own risks. Patients may experience complications such as nausea, vomiting, and respiratory problems. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of any allergies or medical conditions that may increase the risk of anesthesia-related complications.
Risks Associated with Adenoidectomy
In addition to common complications, there are some risks associated specifically with adenoidectomy. These risks include hearing loss, velopharyngeal insufficiency, and hemorrhage.
Hearing Loss
Adenoidectomy may increase the risk of temporary or permanent hearing loss. This is because the adenoids are located near the Eustachian tubes, which are responsible for equalizing pressure in the middle ear. In some cases, the removal of the adenoids may disrupt the function of the Eustachian tubes and lead to hearing problems.
Velopharyngeal Insufficiency
Velopharyngeal insufficiency is a rare but serious complication of adenoidectomy. It occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat are weakened, leading to problems with speech and swallowing. Patients who experience symptoms such as nasal speech, difficulty swallowing, or regurgitation of food should contact their healthcare provider immediately.
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage is a rare but potentially life-threatening complication of adenoidectomy. It occurs when there is uncontrolled bleeding from the surgical site. Patients who experience symptoms such as severe bleeding or difficulty breathing should seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Adenoidectomy in Special Populations
Adenoidectomy in Adults
Adenoidectomy is typically associated with children, but it can also be performed on adults. The procedure is often recommended for adults who experience chronic nasal congestion, snoring, or sleep apnea due to enlarged adenoids. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and typically takes less than an hour.
Recovery time for adults can vary, but most individuals are able to return to work and normal activities within a week. It is important for adults to follow their doctor’s post-operative instructions to reduce the risk of complications.
Considerations for Infants and Younger Children
Adenoidectomy in infants and younger children requires special consideration due to their smaller airways and developing immune systems. The surgery is typically only recommended for children who experience chronic ear infections, breathing problems, or sleep apnea.
Parents should discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with their child’s doctor. It is important to note that adenoids play a role in the immune system, and removing them may increase the risk of infections. However, the benefits of improved breathing and sleep quality may outweigh the risks in certain cases.
Post-operative care for infants and younger children may require additional attention, as they may have difficulty communicating discomfort or following instructions. Parents should closely monitor their child’s recovery and contact their doctor if they have any concerns.
Overall, adenoidectomy can be a safe and effective treatment option for individuals of all ages. However, it is important to carefully consider the risks and benefits for each individual case and to follow post-operative instructions to reduce the risk of complications.
Long-Term Outlook
Benefits of Adenoidectomy
After undergoing an adenoidectomy, patients may experience several benefits in the long term. One of the most significant benefits is improved breathing, especially for those who had difficulty breathing through their nose due to enlarged adenoids. This can lead to better sleep quality and reduced snoring.
Another benefit of adenoidectomy is a reduced risk of ear infections. Enlarged adenoids can block the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid buildup in the middle ear, which can cause ear infections. By removing the adenoids, the risk of ear infections can be significantly reduced.
Adenoidectomy can also help improve sleep apnea symptoms. Enlarged adenoids can obstruct the airway, leading to sleep apnea, a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. By removing the adenoids, the airway can be opened up, reducing the severity of sleep apnea.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After an adenoidectomy, patients will need to follow up with their healthcare provider to ensure proper healing and monitor for any complications. It is essential to keep the surgical site clean and dry and avoid any strenuous activities that may cause bleeding or injury.
Patients may experience some discomfort, such as a sore throat or difficulty swallowing, in the days following the surgery. However, these symptoms should subside within a few days. It is crucial to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding pain management and any prescribed medications.
It is also essential to monitor any changes in breathing, snoring, or sleep quality after the surgery. If any issues arise, patients should contact their healthcare provider immediately. Regular check-ups with the healthcare provider can help ensure that any complications are identified and treated promptly.
In conclusion, adenoidectomy can provide several long-term benefits, including improved breathing, reduced risk of ear infections, and improved sleep apnea symptoms. However, patients must follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding post-operative care and monitoring to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Tonsillectomy: Procedure, Recovery, and Risks
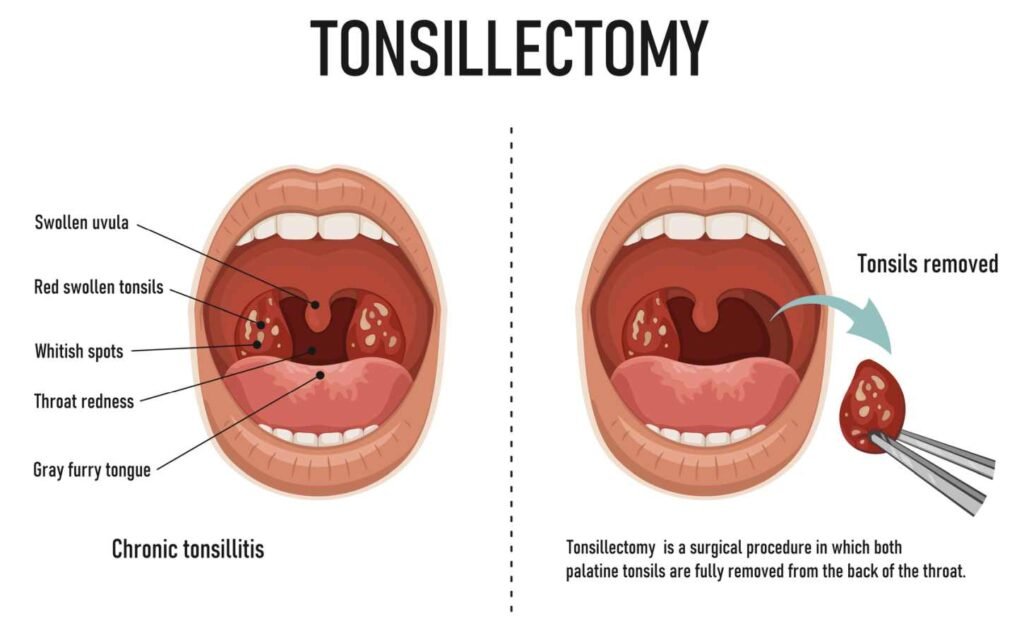
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tonsils. The tonsils are two small glands located at the back of the throat. The purpose of tonsillectomy is to relieve symptoms and improve the overall health of the patient. The surgery is usually performed on an outpatient basis and can be done under local or general anesthesia.
Continue reading: Tonsillectomy: Procedure, Recovery, and Risks