Chronic Insomnia Disorder is a sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide.
Chronic Insomnia Disorder is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and not being able to fall back asleep. Chronic insomnia disorder can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, leading to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating during the day.
There are various causes of chronic insomnia disorder, including stress, anxiety, depression, medical conditions, and certain medications. It is essential to identify the underlying cause of the disorder to effectively treat it. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as improving sleep hygiene and reducing caffeine intake, as well as medication and therapy.
Despite being a common sleep disorder, chronic insomnia disorder is often overlooked and underdiagnosed. It is crucial to seek medical attention if experiencing symptoms of chronic insomnia disorder to prevent long-term health consequences.
Understanding Insomnia
Definition and Types
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. Chronic insomnia disorder is defined as insomnia that occurs at least three nights per week for at least three months. There are two types of insomnia: primary and secondary.
Primary insomnia is not caused by an underlying medical or psychiatric condition, while secondary insomnia is caused by an underlying medical or psychiatric condition.
Etiology and Risk Factors
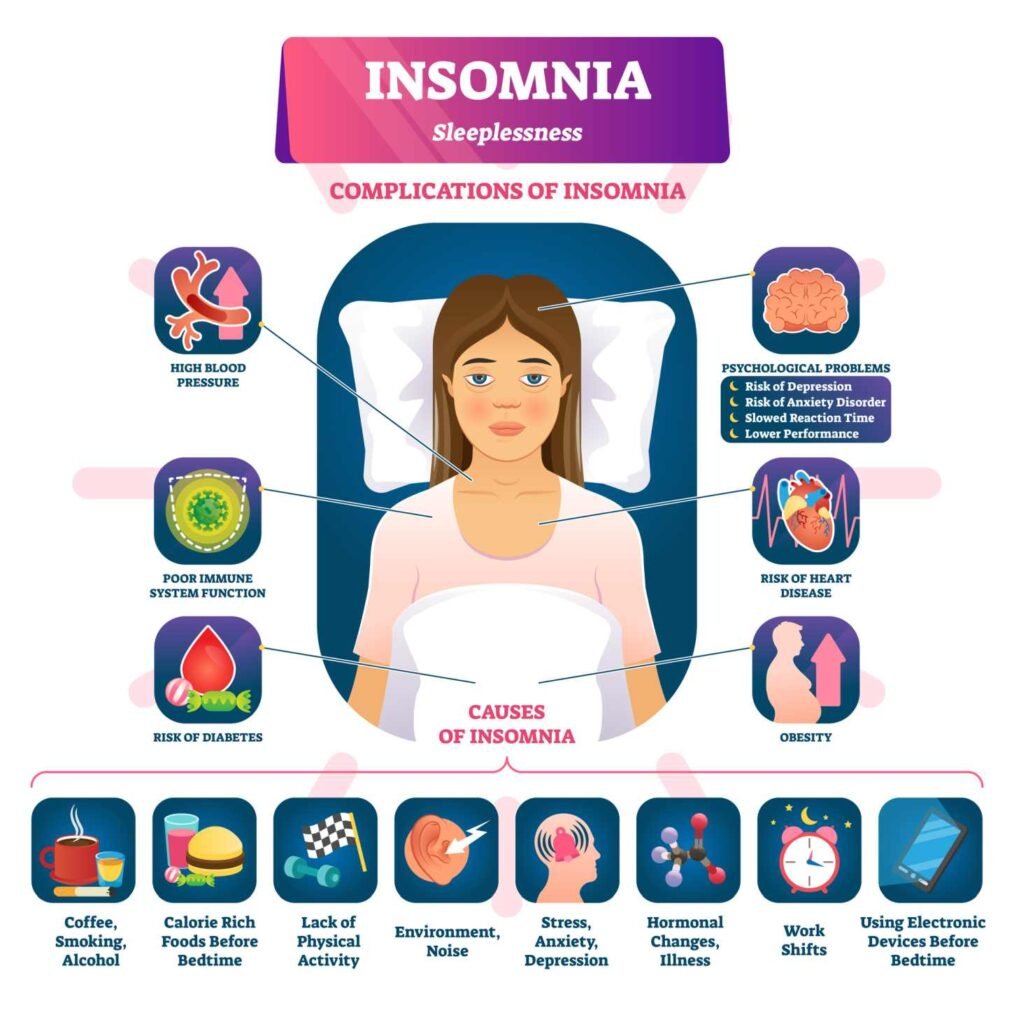
The etiology of insomnia is complex and multifactorial. Some common risk factors for insomnia include stress, anxiety, depression, chronic pain, and certain medications. Other factors that may contribute to insomnia include poor sleep hygiene, irregular sleep schedules, and environmental factors such as noise, light, and temperature.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder, with a prevalence of approximately 10-15% in the general population. Chronic insomnia disorder is less common, with a prevalence of approximately 3-5% in the general population. Insomnia is more common in women than in men, and its prevalence increases with age. Insomnia is also more common in individuals with certain medical and psychiatric conditions, such as chronic pain, anxiety, and depression.
Overall, insomnia is a complex sleep disorder that can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. Understanding the different types of insomnia, as well as the various risk factors and prevalence rates, is important for developing effective treatment strategies.
Identifying Chronic Insomnia
Chronic insomnia is a sleep disorder that affects a significant number of people worldwide. Identifying chronic insomnia can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other sleep disorders or medical conditions. However, there are some key indicators that can help diagnose chronic insomnia.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Third Edition (ICSD-3) defines chronic insomnia disorder as difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, or waking up too early, occurring at least three nights per week for at least three months, and causing significant distress or impairment in daytime functioning.
Individuals with chronic insomnia may experience a range of symptoms, including difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently during the night, waking up too early in the morning, and feeling tired or unrefreshed upon waking. They may also experience daytime symptoms such as fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems.
To diagnose chronic insomnia disorder, a doctor will typically conduct a thorough medical history and physical exam, as well as review the patient’s sleep diary. The sleep diary is a tool that can help track sleep patterns and identify any underlying causes of insomnia, such as stress, caffeine consumption, or medications.
Sleep Diaries and Clinical Assessment
Sleep diaries can be an effective tool for identifying chronic insomnia. A sleep diary typically includes information about the time the patient went to bed, the time they fell asleep, the number of times they woke up during the night, the time they woke up in the morning, and how they felt upon waking.
In addition to sleep diaries, a doctor may also use clinical assessment tools to help diagnose chronic insomnia. These tools may include questionnaires or rating scales that assess the severity of insomnia symptoms and their impact on daytime functioning.
Overall, identifying chronic insomnia requires a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, sleep patterns, and daytime symptoms. With the right diagnosis, individuals with chronic insomnia can receive effective treatment and improve their quality of life.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Chronic insomnia disorder is a condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. These factors can be physical, psychological, or environmental. Understanding the causes of chronic insomnia can help individuals to better manage their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
Physical and Medical Conditions
Physical and medical conditions can contribute to chronic insomnia. These conditions can include chronic pain, respiratory disorders, neurological disorders, and hormonal imbalances. Chronic pain can make it difficult for individuals to fall asleep or stay asleep, while respiratory disorders such as sleep apnea can disrupt sleep quality. Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease can also affect sleep patterns. Hormonal imbalances, such as those associated with menopause, can cause hot flashes and night sweats that can disrupt sleep.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors can also contribute to chronic insomnia. Stress and anxiety are common causes of insomnia. Depression can also affect sleep patterns, causing individuals to have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Additionally, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can cause nightmares and other sleep disturbances.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
Lifestyle and environmental factors can play a role in chronic insomnia. Caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine can all interfere with sleep. Poor diet and lack of exercise can also contribute to insomnia. Environmental factors such as noise, light, and temperature can also affect sleep quality. As individuals age, they may also experience changes in their sleep patterns.
Overall, chronic insomnia is a complex condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. By understanding the causes of chronic insomnia, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
Impact on Health and Quality of Life
Chronic insomnia disorder can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall health and quality of life. This section will explore the various ways in which chronic insomnia disorder can affect an individual’s health and well-being.
Mental Health Correlations
Research has shown that chronic insomnia disorder is strongly correlated with various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Insomnia can exacerbate symptoms of these conditions, leading to a vicious cycle of poor sleep and worsening mental health. Additionally, individuals with chronic insomnia disorder are more likely to experience irritability, decreased concentration, and memory problems.
Physical Health Consequences
Chronic insomnia disorder has also been linked to various physical health consequences. Individuals with insomnia are at an increased risk of developing heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Poor sleep can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illness. Insomnia can also lead to daytime sleepiness and fatigue, which can negatively impact an individual’s productivity and quality of life.
Social and Economic Costs
Chronic insomnia disorder can also have significant social and economic costs. Individuals with insomnia may experience difficulty maintaining relationships, engaging in social activities, and performing well at work. Insomnia can also increase the risk of motor vehicle accidents, leading to potential legal and financial consequences.
In conclusion, chronic insomnia disorder can have a profound impact on an individual’s health and quality of life. It is important for individuals experiencing insomnia to seek treatment in order to mitigate the negative consequences of poor sleep.
Treatment Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a highly effective treatment for chronic insomnia disorder. This therapy focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. CBT-I typically involves several sessions with a therapist, during which the patient learns relaxation techniques, sleep hygiene practices, and how to challenge negative thoughts about sleep. The therapy also includes sleep restriction, which involves limiting the amount of time spent in bed to increase sleep efficiency.
Pharmacologic Treatments
Pharmacologic treatments can be effective for treating chronic insomnia disorder, but they should be used cautiously due to potential side effects and the risk of dependence. Medications commonly used to treat insomnia include melatonin, eszopiclone, ramelteon, zaleplon, and suvorexant. These medications work by either enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA or by targeting the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. It is important to note that medication should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
In addition to CBT-I and pharmacologic treatments, alternative and complementary therapies can also be used to treat chronic insomnia disorder. Relaxation techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which can improve sleep quality. However, the evidence for the effectiveness of these therapies is limited and more research is needed to determine their efficacy.
Overall, the most effective treatment approach for chronic insomnia disorder is a combination of CBT-I and medication, if necessary. It is important for individuals with chronic insomnia disorder to seek the guidance of a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment approach for their specific needs.
Lifestyle Modifications and Self-Care
Chronic insomnia disorder can be a challenging condition to manage, but there are lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies that can help individuals improve their sleep quality and reduce symptoms. Here are some of the most effective strategies:
Sleep Hygiene and Behavioral Changes
One of the most important strategies for managing chronic insomnia disorder is improving sleep hygiene. This involves adopting habits and behaviors that promote healthy sleep, such as:
- Establishing a regular sleep schedule and sticking to it, even on weekends
- Creating a relaxing bedtime routine to help the body wind down before sleep
- Avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime
- Limiting exposure to screens and bright lights in the hours before bed
- Keeping the bedroom cool, quiet, and dark
- Using the bed only for sleep and sex, not for work or other activities
In addition to sleep hygiene, behavioral changes can also be effective for managing chronic insomnia disorder. This might include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to insomnia
- Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery
- Stimulus control therapy, which involves retraining the brain to associate the bed and bedroom with sleep rather than wakefulness
Diet and Physical Activity
Diet and physical activity can also play a role in managing chronic insomnia disorder. Some strategies to consider include:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein
- Avoiding heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, yoga, or swimming, which can help reduce stress and improve sleep quality
- Avoiding intense exercise in the hours leading up to bedtime, as this can be stimulating and make it harder to fall asleep
Overall, lifestyle modifications and self-care strategies can be effective for managing chronic insomnia disorder. By adopting healthy habits and behaviors, individuals can improve their sleep quality and reduce symptoms over time.
Special Considerations
Insomnia in Different Populations
Chronic insomnia disorder affects people of all ages and genders. However, certain populations may be more susceptible to insomnia due to various factors.
Adults and Older Adults
Insomnia is more common in adults and older adults, with up to 50% of adults experiencing symptoms at some point in their lives. Older adults may experience insomnia due to changes in sleep patterns and health conditions such as arthritis and heart disease.
Children and Teens
Insomnia is also prevalent in children and teenagers, with up to 25% of children experiencing sleep difficulties. Factors that may contribute to insomnia in children and teenagers include anxiety, stress, and electronic device use before bedtime.
Women and Pregnancy
Women are more likely to experience insomnia than men, particularly during pregnancy and menopause. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can disrupt sleep, leading to insomnia.
Comorbidities and Secondary Insomnia
Chronic insomnia disorder is often associated with comorbidities, which are other health conditions that may contribute to insomnia. Additionally, insomnia can also be a secondary condition that arises from other sleep-related disorders.
Comorbidities
Comorbidities that may contribute to insomnia include mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression, as well as chronic pain conditions such as arthritis and fibromyalgia. Treatment of the underlying condition may help improve insomnia symptoms.
Sleep-Related Disorders
Insomnia can also be a secondary condition that arises from other sleep-related disorders such as sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome. Treatment of the underlying sleep disorder may help improve insomnia symptoms.
Overall, it is important to consider the unique factors that may contribute to insomnia in different populations and to address any underlying conditions that may be contributing to insomnia symptoms.
Navigating Clinical Practice
Guidelines and Systematic Reviews
When it comes to treating chronic insomnia disorder, healthcare professionals often rely on clinical practice guidelines and systematic reviews to inform their decision-making process. These resources provide evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis, treatment, and management of the disorder.
One such resource is the American Academy of Sleep Medicine’s Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Insomnia in Adults. This guideline provides recommendations for the use of medications in treating chronic insomnia, including the appropriate dosages, potential adverse effects, and monitoring requirements.
Another useful resource is the Cochrane Library’s systematic review on non-pharmacological interventions for chronic insomnia. This review evaluates the effectiveness of various non-pharmacological interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and relaxation techniques, in treating chronic insomnia.
Healthcare professionals should consult these resources when making treatment decisions for patients with chronic insomnia disorder. However, it is important to note that clinical practice guidelines and systematic reviews should not be used as a substitute for clinical judgment or individualized patient care.
Working with Sleep Centers and Specialists
For patients with severe or complex chronic insomnia disorder, referral to a sleep center or specialist may be necessary. Sleep centers can provide comprehensive diagnostic evaluations, including overnight sleep studies, to help identify underlying causes of insomnia.
Sleep specialists can also provide individualized treatment plans, including medication management and behavioral interventions. Collaboration with a sleep center or specialist can help healthcare professionals provide the best possible care for their patients with chronic insomnia disorder.
However, it is important to note that not all patients with chronic insomnia disorder require referral to a sleep center or specialist. Healthcare professionals should use their clinical judgment to determine the appropriate level of care for each individual patient.
In conclusion, navigating clinical practice for chronic insomnia disorder requires a thorough understanding of clinical practice guidelines, systematic reviews, and the role of sleep centers and specialists. Healthcare professionals should use these resources to inform their decision-making process and provide the best possible care for their patients with chronic insomnia disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most effective treatments for chronic insomnia?
There are several treatment options available for chronic insomnia, including medication, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and relaxation techniques. Medications such as benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics can be effective in the short-term, but they can also have side effects and may lead to dependence. CBT, on the other hand, focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can also be helpful in managing insomnia symptoms.
What are the underlying causes of chronic insomnia?
Chronic insomnia can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, medical conditions, and medication use. It can also be a result of poor sleep habits, such as irregular sleep schedules and excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption. Identifying the underlying cause of insomnia is important in determining the most effective treatment approach.
How can insomnia be accurately diagnosed?
Insomnia is typically diagnosed based on a patient’s medical history, sleep habits, and symptoms. A healthcare provider may also order a sleep study to evaluate the patient’s sleep patterns and identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to insomnia.
What lifestyle changes can improve chronic insomnia symptoms?
Making lifestyle changes such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can all help improve chronic insomnia symptoms. Regular exercise and stress-reducing activities, such as yoga or meditation, may also be beneficial.
Is there a connection between mental health and chronic insomnia?
Yes, there is a strong connection between mental health and chronic insomnia. Anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions can contribute to insomnia, and chronic insomnia can also exacerbate these conditions. Addressing any underlying mental health concerns is an important part of managing chronic insomnia.
Can long-term insomnia be completely resolved, and if so, how?
While it may not be possible to completely resolve long-term insomnia, it can be effectively managed with the right treatment approach. This may include a combination of medication, CBT, and lifestyle changes. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the underlying causes of insomnia.
MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin Review: Do They Work?

These gummies are designed to promote relaxation and support sleep quality for adults. Unlike many other sleep aids, they don’t contain melatonin, so you won’t wake up feeling groggy or drowsy.
Continue reading: MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin
Master the 4-7-8 Breathing Technique for Better Sleep

Developed by Dr. Andrew Weil, this technique is designed to promote relaxation and calm the mind, making it easier to drift off to sleep.
The 4-7-8 breathing exercise, also known as the “Relaxing Breath,” is a method that involves a specific pattern of inhaling, holding, and exhaling the breath.
Continue reading: Master the 4-7-8 Breathing Technique for Better Sleep





