Mixed sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that combines the symptoms of both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea.
The condition is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, which can lead to a variety of health issues if left untreated. Mixed sleep apnea is relatively rare compared to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA), but it can still have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
Sleep apnea is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when a person’s breathing is interrupted during sleep, causing them to wake up repeatedly throughout the night. Symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
Mixed sleep apnea is a less common form of the disorder, but it can be just as debilitating as OSA or CSA. Symptoms of mixed sleep apnea include loud snoring, pauses in breathing during sleep, and daytime fatigue. If left untreated, mixed sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breathing during sleep. There are three types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and mixed sleep apnea.
What is Mixed Sleep Apnea?
Mixed sleep apnea is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It is a less common type of sleep apnea, but it can be more severe than either obstructive or central sleep apnea alone.
During mixed sleep apnea, the airway becomes blocked, causing the individual to stop breathing for a period of time. This pause in breathing is then followed by a period of shallow breathing or no breathing at all. Mixed sleep apnea is often more difficult to treat than either obstructive or central sleep apnea alone.
Comparison of OSA, CSA, and Mixed Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea and occurs when the airway becomes blocked during sleep. This can be due to excess weight, enlarged tonsils, or other factors.
In central sleep apnea (CSA), the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. This results in a pause in breathing during sleep.
Mixed sleep apnea is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It is often more severe than either type of sleep apnea alone and can be more difficult to treat.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have sleep apnea. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, and the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine.
Causes and Risk Factors
Anatomical Factors
Mixed sleep apnea can be caused by anatomical factors such as the size and shape of the airway. The airway can become obstructed due to enlarged tonsils, a deviated septum, or a narrow throat. In addition, inadequate muscle tone in the tongue and throat can cause the airway to collapse during sleep, leading to breathing difficulties.
Neurological Factors
Neurological factors can also contribute to mixed sleep apnea. For instance, conditions that affect the central nervous system such as Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis can interfere with breathing during sleep. Additionally, brain injuries or abnormalities that affect the respiratory control center can also cause sleep apnea.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle and environmental factors can increase the risk of mixed sleep apnea. Obesity is a major risk factor as it can lead to the accumulation of fatty tissues around the airway, making it difficult to breathe. Smoking and alcohol consumption can also contribute to the development of sleep apnea by irritating the airway and causing inflammation. High altitude can also increase the risk of sleep apnea due to the lower oxygen levels in the air.
Other risk factors for mixed sleep apnea include heart failure, a family history of sleep apnea, and age. It is important to note that while these factors can increase the likelihood of developing sleep apnea, not everyone with these risk factors will develop the condition.
Signs and Symptoms
Mixed sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that can cause a range of symptoms. Understanding these symptoms is crucial to getting an accurate diagnosis and starting treatment. In this section, we’ll explore the signs and symptoms of mixed sleep apnea, including how to recognize apnea events, the impact of daytime symptoms, and common nocturnal symptoms.
Recognizing Apnea Events
One of the most common signs of mixed sleep apnea is snoring. However, not all snoring is indicative of sleep apnea. In mixed sleep apnea, snoring is often accompanied by pauses in breathing, which can be alarming to those around the affected person. These pauses can last for several seconds and may be followed by gasping or choking sounds as the person tries to catch their breath.
Daytime Impacts
Mixed sleep apnea can have a significant impact on daytime functioning. People with mixed sleep apnea often experience excessive daytime sleepiness, which can make it difficult to concentrate, work, or perform daily tasks. They may also experience morning headaches, dry mouth, and irritability.
Nocturnal Symptoms
Nocturnal symptoms of mixed sleep apnea can include restlessness, frequent awakenings, and difficulty falling asleep. People with mixed sleep apnea may also experience sweating during the night and a feeling of suffocation or choking.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs and symptoms of mixed sleep apnea is crucial to getting an accurate diagnosis and starting treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Diagnosis of Mixed Sleep Apnea
Mixed sleep apnea is a type of sleep apnea that is characterized by a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. It is important to diagnose mixed sleep apnea early on as it can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
Sleep Study and Polysomnography
The first step in diagnosing mixed sleep apnea is to undergo a sleep study. A sleep study, also known as a polysomnography, is a non-invasive test that monitors various physiological functions during sleep. During the test, the patient is hooked up to equipment that measures brain activity, eye movement, heart rate, blood oxygen level, and other vital signs. This data is then used to diagnose sleep disorders such as mixed sleep apnea.
Consultation with a Sleep Specialist
After the sleep study, the patient will typically meet with a sleep specialist to discuss the results and receive a diagnosis. A sleep specialist is a doctor who has specialized training in sleep medicine. They will review the results of the sleep study and may recommend further testing or treatment.
Monitoring Blood Oxygen Levels
One of the key indicators of mixed sleep apnea is a drop in blood oxygen levels during sleep. To monitor blood oxygen levels, a device called a pulse oximeter may be used. This device is attached to the patient’s finger and measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. If the levels drop below a certain threshold, it may indicate the presence of mixed sleep apnea.
In conclusion, diagnosing mixed sleep apnea involves undergoing a sleep study, consulting with a sleep specialist, and monitoring blood oxygen levels. It is important to diagnose and treat mixed sleep apnea early on to prevent serious health issues.
Treatment Strategies
Mixed sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that requires proper treatment to improve the quality of life of affected individuals. The treatment strategies for mixed sleep apnea include:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is a common treatment option for mixed sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose and/or mouth during sleep, which delivers a continuous flow of air to keep the airway open. CPAP is highly effective in reducing the frequency and severity of apnea events and improving sleep quality.
Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP)
Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP) is similar to CPAP but allows for different air pressure levels during inhalation and exhalation. BiPAP is often recommended for patients who have difficulty tolerating CPAP or who require higher air pressure levels to maintain an open airway.
Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV)
Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV) is a newer treatment option that uses a machine to monitor breathing patterns and adjust air pressure levels accordingly. ASV is particularly effective for patients with central sleep apnea, which is a type of sleep apnea that is caused by a lack of respiratory effort.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions may be considered for patients with severe mixed sleep apnea who do not respond to other treatments. The most common surgical procedures for sleep apnea include uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), which involves removing excess tissue from the throat, and maxillomandibular advancement (MMA), which involves moving the upper and/or lower jaw forward to increase the size of the airway.
Lifestyle Modifications and Medications
Lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and sleeping on one’s side can also help improve symptoms of mixed sleep apnea. Medications such as stimulants and antidepressants may also be prescribed to help improve breathing during sleep.
Overall, the treatment strategies for mixed sleep apnea are highly effective in reducing the frequency and severity of apnea events and improving sleep quality. It is important for individuals with mixed sleep apnea to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for their specific needs.
Complications and Comorbidities
Cardiovascular Complications
Mixed sleep apnea can have significant effects on the cardiovascular system, leading to a range of complications and comorbidities. One of the most common complications is hypertension, which can be caused by the repeated episodes of hypoxia and arousal that occur during apneic events. This can increase the risk of developing heart disease, including congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
Studies have also shown that mixed sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of stroke. This may be due to the fact that apneic events can lead to changes in blood pressure and blood flow, which can increase the risk of blood clots and other cardiovascular events.
Effects on Mental Health
Mixed sleep apnea can also have a significant impact on mental health. One of the most common effects is fatigue, which can be caused by the disrupted sleep patterns that occur during apneic events. This can lead to a range of other problems, including difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and mood swings.
In addition to these effects, mixed sleep apnea has also been linked to a range of behavior problems, including depression and anxiety. This may be due to the fact that apneic events can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to changes in brain chemistry and hormone levels.
Impact on Daily Living
Finally, mixed sleep apnea can also have a significant impact on daily living. This may be due to the fact that the symptoms of the condition can make it difficult to engage in normal activities, such as work, socializing, and exercise.
For example, fatigue and other symptoms can make it difficult to concentrate at work, leading to decreased productivity and increased errors. Similarly, the impact on mental health can make it difficult to socialize and engage in other activities, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
In summary, mixed sleep apnea can have a range of complications and comorbidities, including cardiovascular complications, effects on mental health, and impact on daily living. It is important for individuals with the condition to seek appropriate treatment in order to manage these symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Living with Mixed Sleep Apnea
Individuals with mixed sleep apnea face unique challenges when it comes to managing their condition. However, with proper treatment and support, it is possible to improve overall quality of life.
Managing Treatment
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is a common treatment for mixed sleep apnea. This involves wearing a mask over the nose and/or mouth during sleep, which delivers a constant stream of air to keep the airway open. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to find the appropriate pressure setting and mask type for the individual.
In some cases, supplemental oxygen may also be necessary to improve breathing and reduce the risk of complications. However, it is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding oxygen use, as too much oxygen can be harmful.
Lifestyle changes can also be helpful in managing mixed sleep apnea. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime, and treating nasal congestion can all improve symptoms.
Support and Resources
Living with mixed sleep apnea can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. It is important to seek support from loved ones and healthcare professionals. Support groups and online forums can also provide a sense of community and understanding.
There are also resources available to help individuals manage their condition. For example, some CPAP machines have built-in data tracking features to monitor treatment progress. Lung function tests and blood pressure checks can also help monitor overall health.
Despite the challenges, it is possible to live a fulfilling life with mixed sleep apnea. By working closely with healthcare providers, making lifestyle changes, and seeking support, individuals can improve their symptoms and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of mixed sleep apnea?
Mixed sleep apnea is a condition that combines features of both obstructive and central sleep apnea. Common symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, difficulty staying asleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, and morning headaches.
How is mixed sleep apnea diagnosed and classified?
Mixed sleep apnea is diagnosed through a sleep study, which measures breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and other factors during sleep. It is classified based on the severity of the condition, as well as the underlying causes.
What treatments are available for mixed sleep apnea?
Treatment options for mixed sleep apnea may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and sedatives, as well as the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines, oral appliances, and surgery in some cases.
How does mixed sleep apnea differ from central sleep apnea?
Mixed sleep apnea differs from central sleep apnea in that it involves both obstructive and central components. Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by a physical blockage of the airway, while central sleep apnea is caused by a failure of the brain to signal the muscles to breathe.
Can mixed sleep apnea be completely cured or managed effectively?
While there is no cure for mixed sleep apnea, it can be managed effectively with proper treatment. Many people are able to achieve significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life with the use of CPAP machines, oral appliances, and other therapies.
What are the potential causes or risk factors for developing mixed sleep apnea?
Risk factors for mixed sleep apnea may include obesity, smoking, alcohol and sedative use, and certain medical conditions such as heart failure and stroke. It is important to note that anyone can develop mixed sleep apnea, regardless of age or gender.
Hypopnea: Definition, Causes, and Treatment
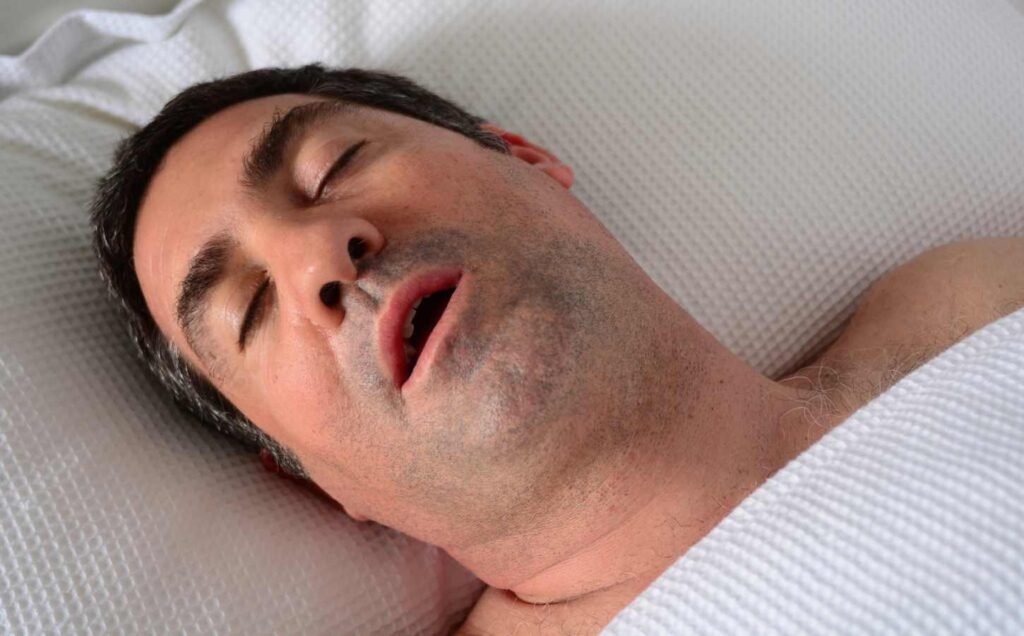

Hypopnea is a sleep-related breathing disorder that is characterized by shallow or slow breathing, resulting in a reduction of airflow into the lungs. Unlike apnea, which is a complete cessation of breathing, hypopnea is a partial obstruction of the airway that leads to a decrease in the amount of oxygen that reaches the body’s vital organs.
Continue reading: Hypopnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
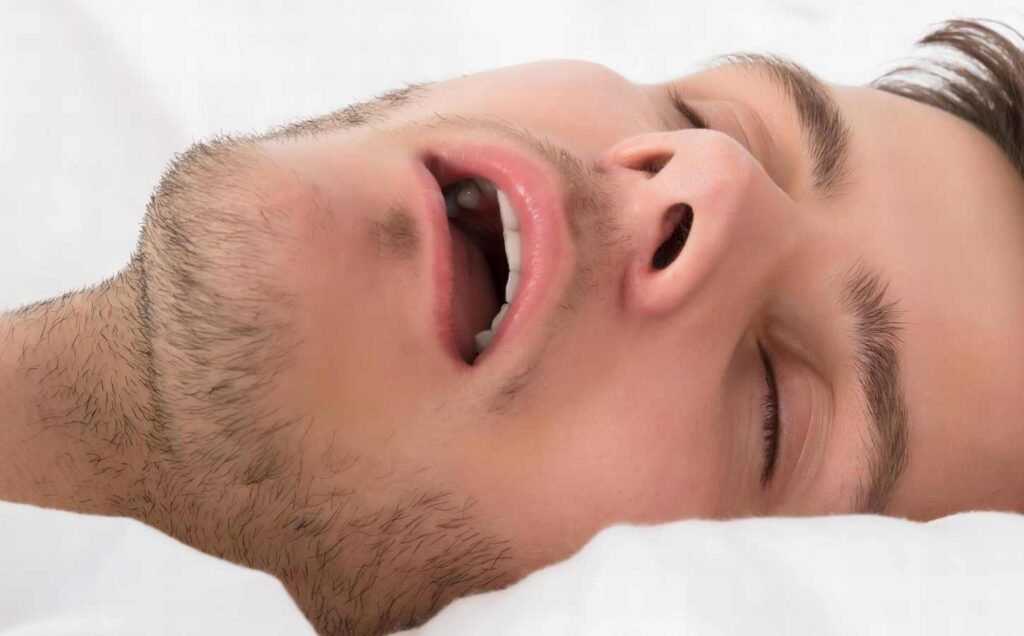

Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by partial or complete obstruction of the upper airway during sleep, leading to repetitive episodes of apnea (cessation of breathing) and hypopnea (reduction in breathing).
Continue reading: Obstructive Sleep Apnea
The Apnea-Hypopnea Index: Definition and Importance
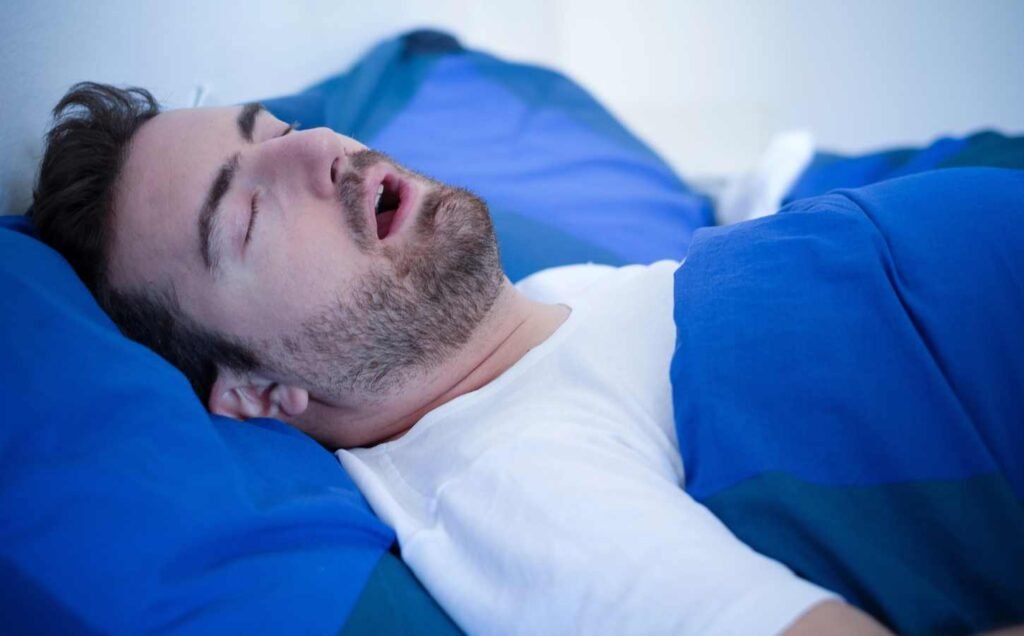

The Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) is a measure of the severity of sleep apnea. It is the number of apneas and hypopneas that occur per hour of sleep. Apneas are complete pauses in breathing that last for at least 10 seconds, while hypopneas are partial reductions in breathing that last for at least 10 seconds and are associated with a decrease in oxygen saturation. AHI is an important measure because sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
Continue reading: The Apnea-Hypopnea Index