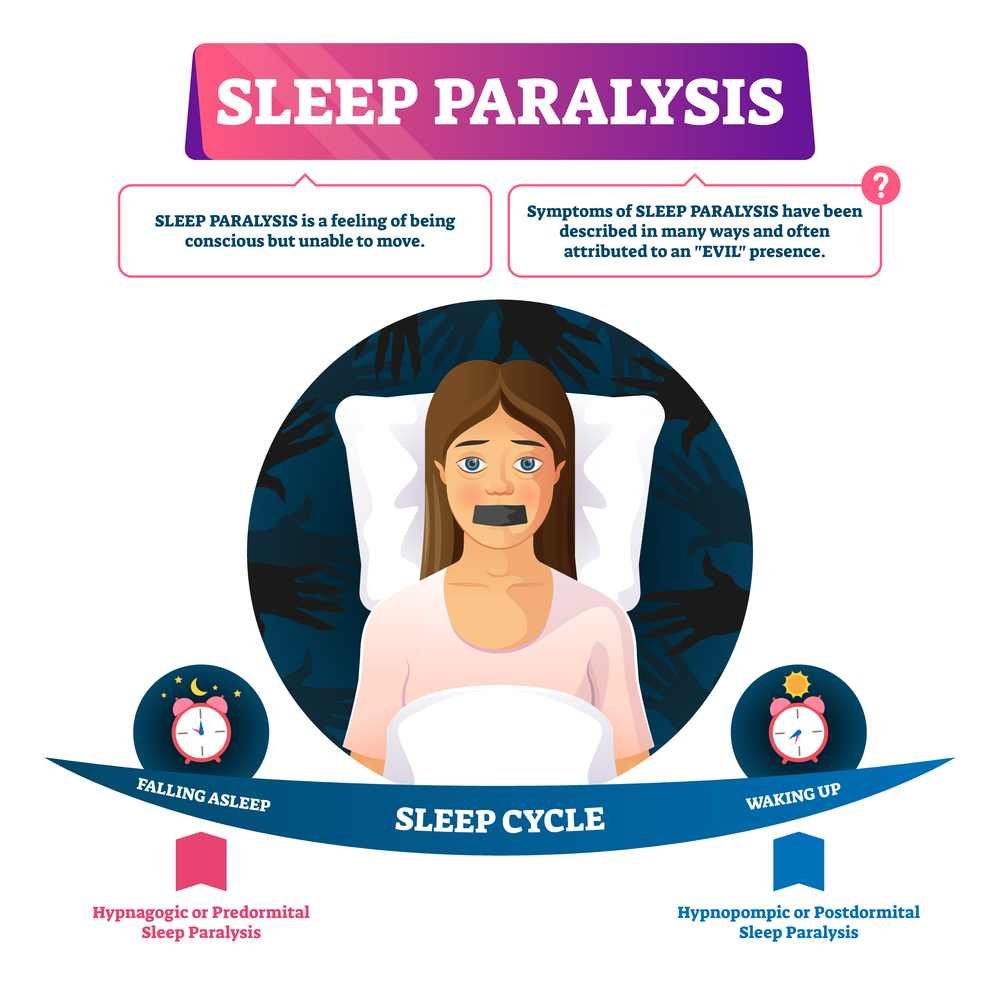
Sleep paralysis is a phenomenon that affects many people around the world.
Sleep paralysis occurs when a person is either falling asleep or waking up and finds themselves unable to move or speak. This temporary paralysis usually lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes and can be a frightening experience for those who go through it.
During sleep paralysis, the individual is fully conscious but unable to move their muscles due to a condition called atonia, which is a natural occurrence during REM sleep. This atonia is meant to prevent the body from acting out dreams, but in the case of sleep paralysis, it can persist even after the individual has woken up. This can lead to feelings of panic and fear, especially if the person also experiences hallucinations during the episode.
While sleep paralysis is not harmful in itself, it can be a symptom of other underlying sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, and insomnia. It is important for individuals who experience frequent episodes of sleep paralysis to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying conditions. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and reduce the frequency of sleep paralysis episodes.
Causes and Risk Factors
Sleep paralysis is a condition that occurs when a person is unable to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. The exact cause of sleep paralysis is not fully understood, but there are several factors that can contribute to its development.
Influence of Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, insomnia, and parasomnia can increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. These conditions can disrupt the normal sleep cycle, leading to episodes of sleep paralysis.
Lifestyle and Environmental Triggers
Certain lifestyle and environmental factors can also trigger sleep paralysis. Stress, alcohol consumption, caffeine intake, jet lag, shift work, sleep deprivation, lack of sleep, and disrupted sleep schedules can all contribute to the development of sleep paralysis.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors such as anxiety, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder, depression, panic disorder, bipolar disorder, and other mental health conditions can also increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Genetic and Physiological Factors
There may also be a genetic predisposition to sleep paralysis, as some families have a higher incidence of the condition. Additionally, underlying medical conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and other neurological disorders can also increase the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
In conclusion, while the exact cause of sleep paralysis is not fully understood, there are several factors that can contribute to its development. By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take steps to reduce their likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment
Medical Assessment and Diagnosis
Sleep paralysis is a condition that can be diagnosed by a healthcare provider or a sleep specialist. The diagnosis may involve a physical examination and an evaluation of the patient’s medical history. In some cases, a sleep study, such as polysomnography, may be recommended to evaluate the patient’s sleep patterns.
Preventative Strategies
There are several strategies that can be employed to prevent sleep paralysis. One of the most effective strategies is to maintain good sleep hygiene. This includes establishing a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, and creating a relaxing sleep environment.
Relaxation techniques, such as meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and deep breathing exercises, can also be helpful in preventing sleep paralysis. Sleeping in a comfortable position, such as on the side, may also reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
Therapeutic Interventions
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that can be used to treat sleep paralysis. CBT focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors that may contribute to sleep problems. Medications such as antidepressants, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may also be prescribed to treat sleep paralysis.
In addition to therapy and medication, support from family and friends can also be beneficial in managing sleep paralysis. It is important for individuals with sleep paralysis to seek treatment and support to improve their sleep habits and overall well-being.

10-3-2-1-0 Sleep Rule: A Simple Guide to Better Sleep

The 10-3-2-1-0 sleep rule is designed to help individuals maintaining a regular sleep schedule that promotes restful and restorative sleep. By following this rule, individuals can create a relaxing environment that signals to the body that it is time to sleep.
Continue reading about the: 10-3-2-1-0 Sleep Rule
MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin Review: Do They Work?

These gummies are designed to promote relaxation and support sleep quality for adults. Unlike many other sleep aids, they don’t contain melatonin, so you won’t wake up feeling groggy or drowsy.
Continue reading: MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin



