Sleep-wakefulness disorder is a condition that affects an individual’s ability to maintain a normal sleep-wake cycle.
Sleep-wakefulness disorder can cause a wide range of symptoms, including insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, and difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Sleep-wakefulness disorder can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, affecting their ability to perform daily activities and maintain relationships.
Sleep disorders, including sleep-wakefulness disorder, are becoming increasingly common in today’s society. Factors such as stress, poor sleep habits, and technology use can all contribute to the development of sleep disorders. Additionally, certain medical conditions and medications can also contribute to the development of sleep-wakefulness disorder. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms of sleep-wakefulness disorder to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Understanding Sleep-Wakefulness Disorders
Defining Sleep-Wake Disorders
Sleep-wakefulness disorders refer to a group of conditions that affect the quality, timing, and duration of sleep. These disorders can cause significant disruptions to an individual’s daily routine, leading to fatigue, reduced productivity, and impaired cognitive function. Sleep-wake disorders are often characterized by abnormal sleep patterns, including difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early.
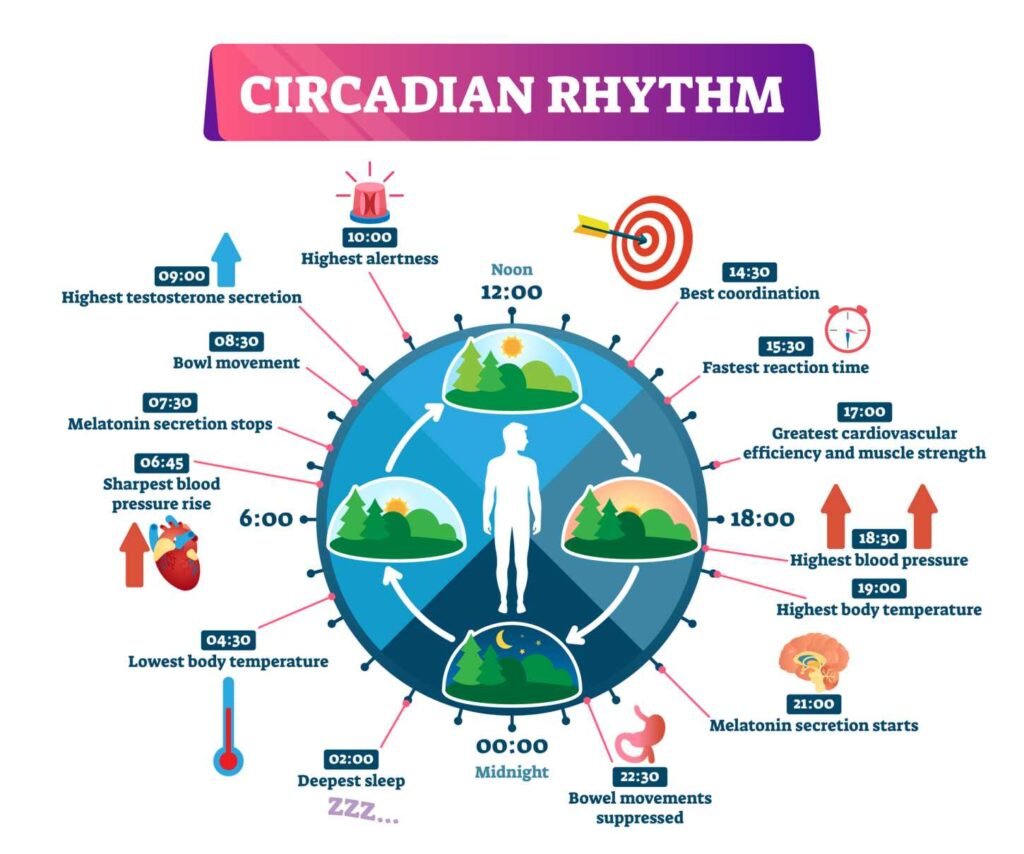
Circadian Rhythm and Its Role
The sleep-wake cycle is controlled by the body’s internal clock, also known as the circadian rhythm. This rhythm regulates the timing of various physiological processes, including sleep and wakefulness. The circadian rhythm is influenced by external cues, such as light and temperature, and can be disrupted by factors such as shift work, jet lag, and irregular sleep schedules.
Categories of Sleep-Wake Disorders
There are several categories of sleep-wake disorders, each with its own unique set of symptoms and diagnostic criteria. These categories include circadian rhythm sleep disorders, non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder, delayed sleep-wake phase disorder, advanced sleep-wake phase disorder, and irregular sleep-wake rhythm disorder.
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders are characterized by disruptions to the normal timing of the sleep-wake cycle.
Non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder is a rare condition in which an individual’s circadian rhythm is longer than 24 hours, leading to a gradual shift in the sleep-wake cycle over time.
Delayed sleep-wake phase disorder is a condition in which an individual’s sleep-wake cycle is delayed by several hours, making it difficult to fall asleep and wake up at the desired times.
Advanced sleep-wake phase disorder is the opposite of delayed sleep-wake phase disorder, with an individual’s sleep-wake cycle occurring earlier than desired.
Irregular sleep-wake rhythm disorder is a condition in which an individual’s sleep occurs in multiple episodes throughout the day and night, with no clear pattern or regularity.
In conclusion, understanding sleep-wakefulness disorders is crucial for individuals with disrupted sleep patterns. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the negative impact of these disorders on their daily routines.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic and Biological Factors
Several genetic and biological factors can contribute to sleep-wakefulness disorder. Individuals with a family history of the disorder are at a higher risk of developing it. Studies have also shown that certain genes can influence an individual’s circadian rhythm, which can lead to sleep-wakefulness disorder.
Moreover, certain medical conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and sleep apnea can also cause disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle. Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during menopause, can also contribute to the disorder.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors can also play a role in the development of sleep-wakefulness disorder. Exposure to bright light at night, such as from electronic devices, can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Shift work and jet lag can also cause disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle, leading to the disorder.
Lifestyle and Health Conditions
Lifestyle factors such as stress, age, obesity, and substance use can also contribute to sleep-wakefulness disorder. Chronic stress can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, while aging can lead to changes in the circadian rhythm. Obesity can also cause disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle, as can the use of alcohol, caffeine, and other substances.
Certain health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can also cause disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle and contribute to the disorder. It is important for individuals with these conditions to seek treatment to manage their symptoms and improve their sleep quality.
Signs and Symptoms
Common Symptoms
Individuals with sleep-wakefulness disorder experience a range of symptoms that can significantly impact their daily life. One of the most common symptoms is fatigue, which can lead to difficulty concentrating and decreased productivity. Daytime sleepiness is also a common symptom, which can make it challenging to stay awake during the day and may result in falling asleep at inappropriate times.
Another common symptom is difficulty falling asleep, which can lead to insomnia and further exacerbate daytime sleepiness. Mood disturbances, such as anxiety and depression, are also common in individuals with sleep-wakefulness disorder. These symptoms can be further exacerbated by the lack of restful sleep, leading to a vicious cycle of poor sleep and poor mental health.
Behavioral and Cognitive Impact
Sleep-wakefulness disorder can also have a significant impact on an individual’s behavior and cognitive abilities. Alertness and attention may be impaired, leading to poor performance at work or school. Memory difficulty is also common, which can further impact daily functioning.
Poor motor skills may also be a symptom of sleep-wakefulness disorder, making it challenging to perform tasks that require coordination and dexterity. These symptoms can lead to frustration and reduced quality of life for individuals with sleep-wakefulness disorder.
In summary, sleep-wakefulness disorder is characterized by a range of symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. While fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and difficulty falling asleep are common symptoms, mood disturbances and cognitive impairments can also occur. It is important for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and Assessment
Medical Evaluation
The diagnosis of sleep-wakefulness disorder requires a comprehensive medical evaluation. A physician will typically perform a physical examination and take a detailed medical history to identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the disorder. The physician may also perform blood tests to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Polysomnography and Sleep Studies
Polysomnography and sleep studies are important diagnostic tools used to evaluate sleep-wakefulness disorder. Polysomnography involves the use of electrodes to monitor brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and muscle activity during sleep. Sleep studies involve monitoring breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and other physiological parameters during sleep.
These tests can help identify the specific type of sleep-wakefulness disorder and determine the severity of the condition. They can also help identify any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the disorder.
Overall, a thorough medical evaluation and the use of diagnostic tools such as polysomnography and sleep studies are essential for the accurate diagnosis and assessment of sleep-wakefulness disorder.
Common Sleep-Wakefulness Disorders
Sleep-wakefulness disorders are a group of conditions that affect the quality, timing, and amount of sleep a person gets. These disorders can cause a wide range of symptoms, including insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, and abnormal sleep behaviors. Here are some of the most common sleep-wakefulness disorders:
Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder that makes it difficult for a person to fall asleep or stay asleep. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, depression, and certain medications. Insomnia can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term), and it can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden, uncontrollable sleep attacks. It is caused by a deficiency of a chemical in the brain called hypocretin, which regulates wakefulness. Narcolepsy can also cause cataplexy (sudden loss of muscle tone), sleep paralysis, and hallucinations.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that causes a person to stop breathing during sleep. There are two types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA is caused by a blockage in the airway, while CSA is caused by a problem with the brain’s respiratory control center. Sleep apnea can cause loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness.
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder that causes an irresistible urge to move the legs, especially at night. RLS can cause discomfort, tingling, or crawling sensations in the legs, which can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. RLS can also cause periodic limb movements during sleep (PLMS), which can disrupt sleep and cause excessive daytime sleepiness.
Parasomnias
Parasomnias are a group of sleep disorders that involve abnormal sleep behaviors, such as sleepwalking, night terrors, and REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). Parasomnias can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, and certain medications. They can also be associated with other sleep-wakefulness disorders, such as narcolepsy and sleep apnea.
In conclusion, sleep-wakefulness disorders can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of these disorders and seek treatment if necessary. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most people with sleep-wakefulness disorders can improve their sleep and reduce their symptoms.
Treatment and Management
Pharmacological Interventions
Pharmacological interventions are often used to treat sleep-wakefulness disorder. Melatonin is a hormone that regulates sleep and wakefulness and is commonly used to treat this disorder. Antidepressants and antihistamines can also be used to treat sleep-wakefulness disorder. However, it is important to note that these medications can have side effects and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Behavioral and Lifestyle Changes
Behavioral and lifestyle changes can also be effective in managing sleep-wakefulness disorder. Relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Sleep hygiene practices such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can also improve sleep quality.
Exercise is another effective way to manage sleep-wakefulness disorder. Regular exercise can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle and promote restful sleep. However, it is important to avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as this can interfere with sleep.
Chronotherapy and Light Therapy
Chronotherapy and light therapy are non-pharmacological interventions that can be used to treat sleep-wakefulness disorder. Chronotherapy involves gradually adjusting the sleep-wake schedule to align with the desired sleep pattern. Light therapy involves exposure to bright light during specific times of the day to regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
Tasimelteon is a medication that specifically targets the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle in individuals with sleep-wakefulness disorder. Bright light therapy can also be effective in regulating the sleep-wake cycle and improving sleep quality.
Overall, a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, including medication, behavioral and lifestyle changes, and chronotherapy and light therapy, can effectively manage sleep-wakefulness disorder. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Special Considerations
Sleep Disorders in Blind Individuals
Blind individuals are at a higher risk of developing sleep-wakefulness disorders than those with normal vision. This is because the absence of light cues can disrupt the body’s natural circadian rhythm, leading to irregular sleep patterns. Blind individuals may experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and waking up at the desired time.
To manage sleep disorders in blind individuals, it is important to establish a consistent sleep schedule and create a sleep-conducive environment. This may involve using a white noise machine, blackout curtains, and avoiding exposure to bright light before bedtime. In some cases, melatonin supplements may be recommended to help regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
Impact on Children and Adolescents
Sleep-wakefulness disorders can have a significant impact on the development and well-being of children and adolescents. Lack of sleep can lead to irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating in school. In addition, sleep disorders can interfere with growth and development, as well as increase the risk of obesity and other health problems.
To promote healthy sleep habits in children and adolescents, it is important to establish a consistent bedtime routine and limit exposure to electronic devices before bedtime. Parents should also encourage regular exercise and a healthy diet to help improve sleep quality. If sleep problems persist, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Prevention and Coping Strategies
Improving Sleep Hygiene
One of the most effective ways to prevent and manage sleep-wakefulness disorder is to improve sleep hygiene. This involves developing good sleep habits that promote restful and uninterrupted sleep. Some tips for improving sleep hygiene include:
- Establishing a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Creating a comfortable sleep environment by keeping the bedroom quiet, cool, and dark.
- Avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime, such as watching TV, using electronic devices, or engaging in intense exercise.
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption, especially in the evening.
- Avoiding large meals before bedtime.
By following these tips, individuals can create a conducive environment for quality sleep, which can help reduce the frequency and severity of sleep-wakefulness disorder symptoms.
Stress Management and Relaxation
Stress is a common trigger for sleep-wakefulness disorder, and learning effective stress management techniques can be helpful in preventing and managing the condition. Some relaxation techniques that can help reduce stress and promote restful sleep include:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Guided imagery
In addition, engaging in regular physical activity can also be helpful in reducing stress and promoting quality sleep. By incorporating stress management and relaxation techniques into their daily routine, individuals can improve their overall sleep quality and reduce the impact of sleep-wakefulness disorder on their daily life.
Implications and Complications
Effects on Mental and Physical Health
Sleep-wakefulness disorder can have significant implications for both mental and physical health. Individuals with this disorder often experience daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. These symptoms can negatively impact an individual’s quality of life, including their ability to perform daily activities and maintain relationships.
In addition to these immediate effects, sleep-wakefulness disorder has also been linked to a number of long-term health complications. Research has shown that individuals with this disorder may be at increased risk for a range of health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and cancer. Additionally, sleep-wakefulness disorder has been associated with an increased risk of accidents, including traffic accidents.
Social and Occupational Consequences
The social and occupational consequences of sleep-wakefulness disorder can also be significant. Individuals with this disorder may experience decreased work efficiency and productivity, which can impact their job performance and career advancement. Additionally, sleep-wakefulness disorder can lead to emotional disturbance, including depression and anxiety, which can further impact an individual’s ability to function in their personal and professional lives.
Furthermore, sleep-wakefulness disorder can also have social consequences, such as strained relationships with family and friends due to irritability and mood swings. It may also lead to social isolation and a decreased quality of life.
Overall, sleep-wakefulness disorder has a significant impact on an individual’s mental and physical health, as well as their ability to function in their personal and professional lives. It is important for individuals with this disorder to seek treatment to manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of long-term health complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of sleep-wakefulness disorders?
The common symptoms of sleep-wakefulness disorders include difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, irregular sleep-wake cycles, and insomnia. People with these disorders may also experience fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating during the day.
How are sleep-wakefulness disorders diagnosed?
A sleep specialist can diagnose sleep-wakefulness disorders through a combination of a patient’s medical history, physical examination, and sleep study. A sleep study involves monitoring brain activity, breathing, and other bodily functions during sleep to help diagnose the specific type of sleep-wakefulness disorder.
What treatments are available for sleep-wakefulness disorders?
Treatment options for sleep-wakefulness disorders include medication, light therapy, and behavioral therapy. Medications such as stimulants and sleep aids can help regulate sleep-wake cycles. Light therapy involves exposure to bright light to help reset the body’s internal clock. Behavioral therapy can help improve sleep habits and promote healthy sleep patterns.
Can lifestyle changes improve sleep-wakefulness disorders?
Yes, lifestyle changes can help improve sleep-wakefulness disorders. Regular exercise, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and creating a relaxing sleep environment can all contribute to better sleep.
What is the impact of psychological factors on sleep-wakefulness disorders?
Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression can worsen sleep-wakefulness disorders. Addressing these underlying issues through therapy or other interventions can improve sleep quality and overall well-being.
Are there any new research findings on sleep-wakefulness disorders?
Ongoing research is exploring new treatments and approaches for sleep-wakefulness disorders. Some studies are investigating the use of virtual reality therapy and non-invasive brain stimulation to improve sleep quality. Other research is examining the impact of sleep-wakefulness disorders on cognitive function and overall health.
MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin Review: Do They Work?

These gummies are designed to promote relaxation and support sleep quality for adults. Unlike many other sleep aids, they don’t contain melatonin, so you won’t wake up feeling groggy or drowsy.
Continue reading: MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin
Master the 4-7-8 Breathing Technique for Better Sleep

Developed by Dr. Andrew Weil, this technique is designed to promote relaxation and calm the mind, making it easier to drift off to sleep.
The 4-7-8 breathing exercise, also known as the “Relaxing Breath,” is a method that involves a specific pattern of inhaling, holding, and exhaling the breath.
Continue reading: Master the 4-7-8 Breathing Technique for Better Sleep





