Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep is an essential part of the sleep cycle that occurs after the initial stage of Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep.
During Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep, the brain waves slow down, and the body temperature drops, preparing the body for deep sleep. Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep typically makes up around 50% of total sleep time in adults and is characterized by the presence of sleep spindles and K-complexes.
Sleep spindles are brief bursts of brain activity that occur during Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep and are thought to play a role in memory consolidation. K-complexes, on the other hand, are large, slow brain waves that occur in response to external stimuli, such as noise. They are believed to help the brain filter out irrelevant information during sleep.
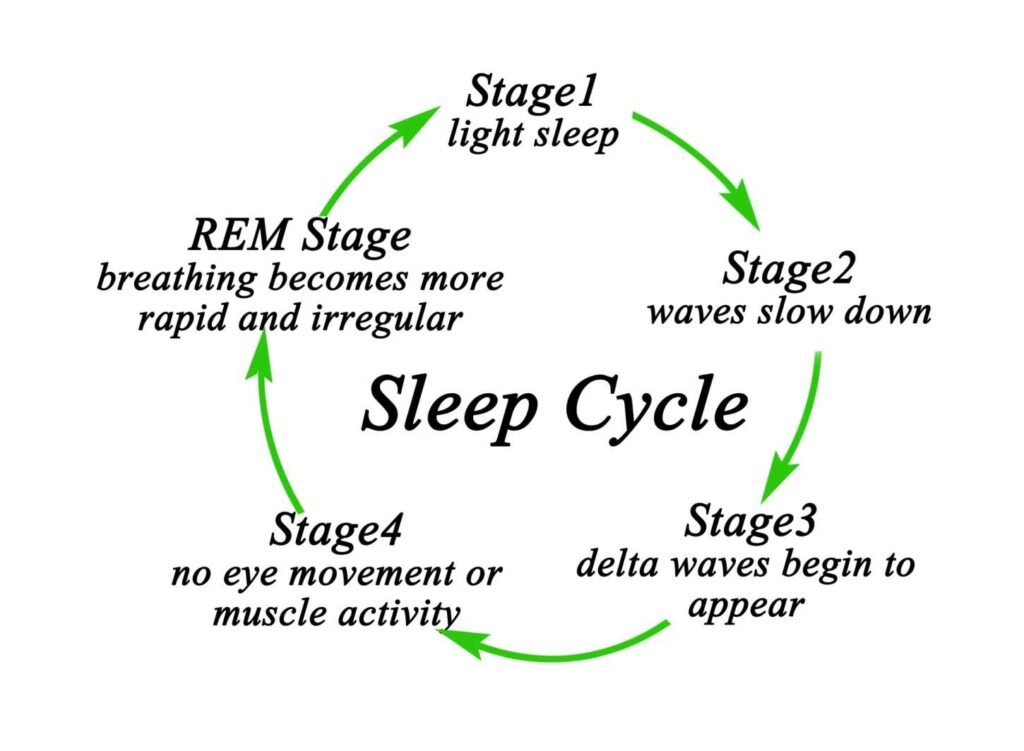
Overall, Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep is a crucial component of the sleep cycle that helps the body and brain recharge and prepare for the next day. Understanding the different stages of sleep and their functions can help individuals prioritize healthy sleep habits and improve overall sleep quality.
Characteristics of Stage 2 NREM Sleep
Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep is the second stage of sleep, following the initial stage of light sleep. It is characterized by specific brain wave patterns, physiological changes, and a role in memory consolidation.
Brain Wave Patterns
During Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep, the brain produces a distinctive pattern of brain waves, including sleep spindles and K-complexes. Sleep spindles are bursts of brain activity that last for a second or two, and occur in the frequency range of 11-16 Hz. K-complexes are sudden, high-amplitude waves that occur in response to external stimuli, such as noise.
Theta waves, which are slower and more synchronized than the alpha waves of Stage 1 Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep, also become prominent during Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep.
Physiological Changes
During Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep, there is a decrease in muscle tone, heart rate, breathing, and temperature. Eye movements cease, and the body becomes less responsive to external stimuli. However, the sleeper can still be awakened easily.
Role in Memory Consolidation
Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep is believed to play a critical role in memory consolidation. Studies have shown that memories are consolidated during sleep, and that sleep spindles are associated with improved memory performance. Sleep spindles are thought to reflect the reactivation of memory traces in the brain, which strengthens the connections between neurons and leads to long-term memory storage.
In conclusion, Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep is characterized by distinctive brain wave patterns, physiological changes, and a critical role in memory consolidation. By understanding the characteristics of this stage of sleep, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms of memory consolidation and potentially develop new treatments for memory-related disorders.
Significance and Functions in the Sleep Cycle
Transition to Deeper Sleep Stages
Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep is a critical phase in the sleep cycle that prepares the body for the deeper stages of sleep. During this stage, the body temperature drops, and the heart rate and breathing slow down. This transition to deeper sleep stages is essential for the body to repair and rejuvenate itself.
Cognitive and Physical Health Implications
Research has shown that Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep plays a crucial role in learning and memory consolidation. It is during this stage that the brain processes and consolidates information gathered during the day. Studies have also linked inadequate sleep quality, including insufficient Stage 2 NREM sleep, to various health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Moreover, Stage 2 Non-Rapid Eye Movement sleep is essential for the secretion of growth hormone, which is vital for tissue repair and growth. Sleep deprivation can impair the secretion of growth hormone, leading to decreased muscle mass and bone density.
In conclusion, Stage 2 NREM sleep is a critical phase in the sleep cycle, facilitating the transition to deeper sleep stages and playing a vital role in learning, memory consolidation, and physical health. It is crucial to prioritize sleep quality to ensure adequate Stage 2 NREM sleep and avoid the negative consequences of sleep deprivation.
Stage 1 Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep
Stage 3 Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep
Stage 3 Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep: Characteristics and Importance

Stage 3 Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep is one of the four stages of NREM sleep, which is characterized by slow brain waves, relaxed muscles, and a decrease in heart rate and breathing.
Continue reading about: Stage 3 Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep
Rapid Eye Movement: Understanding the Sleep Cycle

Understanding the importance of REM sleep is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. In the following article, we will explore the science behind REM sleep, its functions, and the potential consequences of sleep deprivation on REM sleep
Continue reading: Rapid Eye Movement: Understanding the Sleep Cycle
Sleep Spindles and K-Complexes: Understanding Their Roles in Sleep

Sleep spindles and K-complexes are two distinct patterns of brain waves that occur during sleep. They are important components of sleep architecture, which refers to the organization of sleep into distinct stages.
Continue reading about Sleep Spindles and K-Complexes




