Understanding how much sleep one needs is crucial for maintaining health at every age.
What is the right amount of sleep, for your age? Sleep requirements vary significantly from infancy to late adulthood, reflecting the body’s changing needs for rest and recovery. Knowing these needs can help optimize sleep routines and improve overall well-being.
Infants typically require the most sleep, often sleeping 14 to 17 hours a day. As children grow, their needs gradually decrease, with school-aged kids needing about 9 to 11 hours. Adolescents should aim for 8 to 10 hours, while adults generally thrive with 7 to 9 hours each night.
As individuals age, their sleep patterns may shift, leading to potential difficulties in achieving restful sleep. Awareness of age-related sleep needs can guide caregivers and individuals alike in fostering healthier sleep habits that support long-term wellness.
Understanding Sleep and Its Stages
Sleep is a complex physiological process vital for overall health. It involves various stages, each playing a crucial role in maintaining cognitive function, emotional regulation, and physical wellness. The brain transitions between these stages throughout the night, influencing sleep quality.
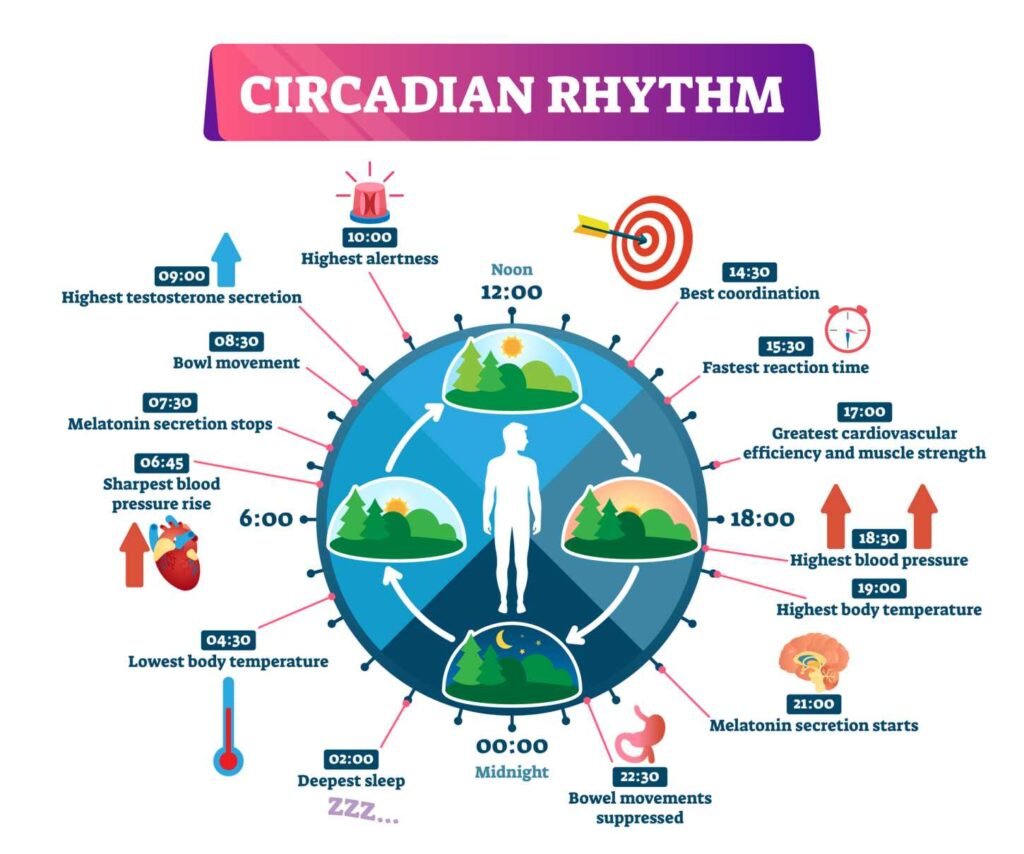
The Science of Sleep
Sleep is regulated by the brain through processes like the release of melatonin and the circadian rhythm. Melatonin, a hormone produced in response to darkness, signals the body to prepare for sleep. The circadian rhythm is the body’s internal clock that dictates sleep-wake cycles, impacting alertness and energy levels.
Research indicates that sleep is essential for memory consolidation and learning. While awake, the brain processes and stores information, but restoration happens during sleep. Insufficient sleep can disrupt these processes, leading to cognitive decline and emotional instability.
Stages of Sleep: REM and Non-REM
Sleep comprises two primary stages: REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and Non-REM. Non-REM sleep includes three stages, progressing from light sleep to deep sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep.
- Non-REM Sleep:
- Stage 1: Light sleep that lasts a few minutes; easy to wake.
- Stage 2: Deeper sleep where heart rate decreases; lasts about 20 minutes.
- Stage 3: Deep sleep; essential for physical restoration and growth.
- REM Sleep:
- Occurs about 90 minutes after falling asleep.
- Associated with vivid dreaming and brain activity similar to being awake.
- Important for emotional resilience and memory processing.
Both stages are vital. Deep sleep enhances physical recovery, while REM sleep supports cognitive functions. Balancing these stages contributes to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
How Sleep Needs Change with Age
Sleep requirements vary significantly across different stages of life. Each age group has specific needs that are essential for growth, development, and overall well-being. Understanding these sleep needs can help individuals optimize their health and daily functioning.
Infants and Sleep Requirements
Infants require a substantial amount of sleep, typically between 14 to 17 hours daily. Sleep patterns in this age group are irregular, with many waking frequently for feeding. During the early months, newborns may sleep up to 18 to 20 hours, as sleep is crucial for their growth and cognitive development.
Sleep contributes significantly to brain development, facilitating critical processes such as memory consolidation and learning. Establishing a consistent sleep routine can aid in better sleep quality as they grow.

Sleep in Toddlers and Preschoolers
Toddlers, aged 1 to 3 years, generally need about 11 to 14 hours of sleep, including naps. As they progress into preschool age, the requirement remains around 10 to 13 hours. This period is vital for developmental milestones, where sleep supports both physical growth and cognitive processing.
Inadequate sleep can lead to behavioral issues and hinder learning abilities in preschoolers. Maintaining a structured bedtime routine can help toddlers and preschoolers feel secure and ready for sleep.
Children and Their Sleep Needs
School-age children, between 6 to 13 years, typically require 9 to 11 hours of sleep. This amount of sleep supports their academic performance, emotional regulation, and growth. As children engage in more structured activities and schooling, consistent sleep patterns become increasingly important.
Quality sleep during this stage is linked to better concentration and memory. Parents should encourage good sleep hygiene practices, such as limiting screen time before bed, to improve sleep quality.
Teenagers and Adequate Sleep
Teenagers require about 8 to 10 hours of sleep, but many often get less due to academic pressures and social activities. Adolescence is marked by significant physical and psychological changes; thus, adequate sleep is essential for health and development.
Sleep deprivation can impact a teen’s mood, academic performance, and overall health. Educating teens about the importance of sleep can foster healthier habits and improve their daily functioning.
Adults and Optimal Sleep Duration
Adults, aged 18 to 64 years, generally need 7 to 9 hours of sleep for optimal health and performance. Maintaining this amount supports a range of functions, including cognitive abilities, mood regulation, and physical well-being.
Unfortunately, many adults experience sleep disturbances due to stress and lifestyle factors. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene, such as creating a comfortable sleep environment and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, is important.
Seniors and Sleep Patterns
Seniors, aged 65 and older, typically need about 7 to 8 hours of sleep. As individuals age, they often experience changes in sleep architecture, leading to lighter sleep and more frequent awakenings.
This age group may also face various health issues that impact sleep quality. It is critical for seniors to establish regular sleep schedules and engage in relaxing activities before bed to improve sleep cohesion and quality.
Factors Affecting Sleep Quality
Multiple elements can significantly impact sleep quality. Understanding these factors is essential for improving sleep hygiene and achieving restorative rest.
Sleep Disorders and Their Impact
Sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea are prevalent issues that can severely affect sleep quality. Insomnia involves difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. This leads to daytime fatigue and impaired function.
Sleep apnea, characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep, can cause fragmented sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness. Both disorders often require medical evaluation and treatment to restore healthy sleep patterns. Recognizing and addressing these conditions is crucial for achieving better sleep quality.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle choices and environmental conditions play a vital role in sleep quality. Factors such as irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen time, and inadequate sleep hygiene can hinder restful sleep.
Moreover, the sleeping environment affects a person’s ability to fall and stay asleep. Noise, light, and temperature can create distractions. Creating a calm and conducive environment can significantly enhance sleep quality.
Diet, Exercise, and Sleep
Diet and exercise significantly influence sleep patterns. Consuming heavy meals, caffeine, or alcohol close to bedtime can disrupt sleep. Foods rich in tryptophan, such as turkey and nuts, can promote better sleep.
Regular physical activity is beneficial but timing matters. Engaging in vigorous exercise shortly before bedtime may energize rather than relax. Conversely, moderate exercise during the day can help improve sleep quality and facilitate a deeper rest.
Emotional Health and Its Influence on Sleep
Emotional health directly affects sleep quality. High levels of stress, anxiety, or depression can lead to difficulties with sleep onset and maintenance. Chronic stress activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, keeping individuals awake and alert.
Practices such as mindfulness and relaxation techniques can alleviate these emotional burdens. Addressing mental health is crucial for improving overall sleep quality. Taking proactive steps could lead to more restful nights and better daytime functioning.
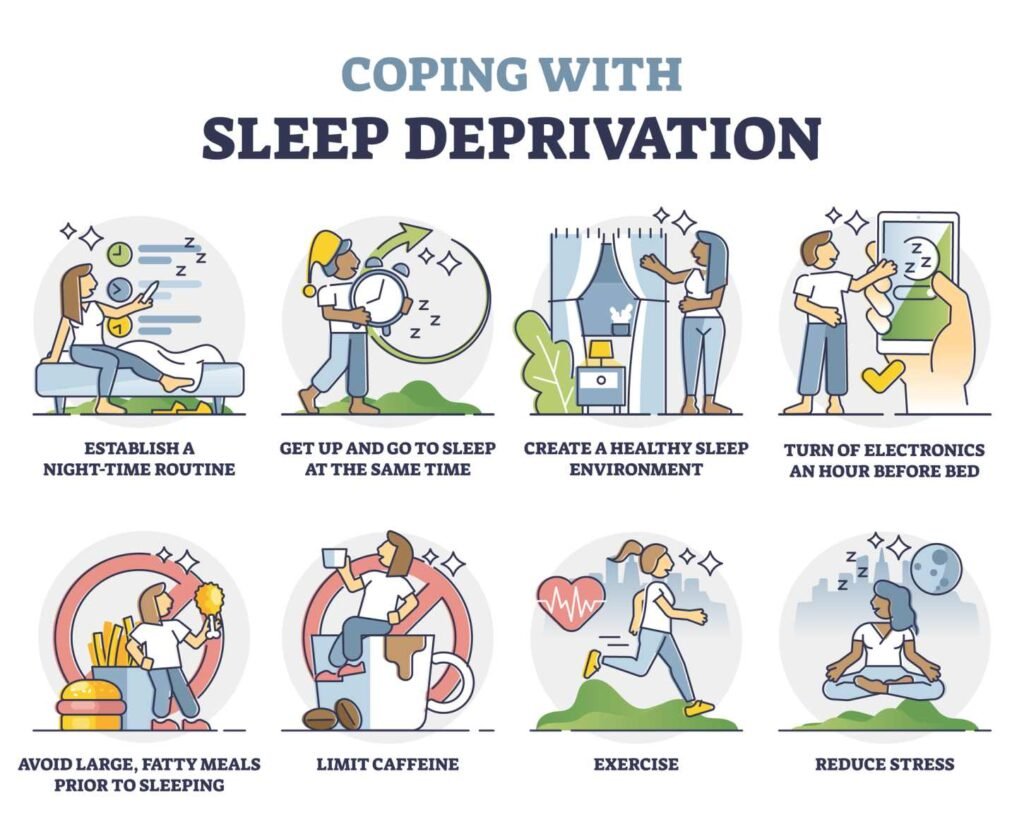
Risks of Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation poses significant risks that can affect physical health, mental well-being, and cognitive performance. It is essential to recognize these potential consequences to emphasize the importance of adequate sleep.
Short-Term and Long-Term Health Consequences
In the short term, sleep deprivation can lead to increased irritability, mood swings, and impaired focus. Individuals may find it difficult to concentrate on tasks, resulting in decreased productivity.
Long-term sleep deprivation can exacerbate health issues, including high blood pressure, obesity, and increased risk of chronic diseases. Chronic inflammation may also occur, affecting the body’s immune response and potentially leading to serious conditions like heart disease and stroke.
Sleep Deprivation and Chronic Diseases
Research indicates a strong link between sleep deprivation and chronic diseases. Individuals who consistently lack sufficient sleep are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Disruptions in insulin sensitivity may occur when sleep is compromised.
Moreover, sleep deprivation is connected to conditions like depression and anxiety. Studies suggest that insufficient sleep can create a cycle where mental health problems worsen, further affecting sleep quality and duration. This cycle can ultimately contribute to chronic diseases and overall reduced health.
The Cognitive Cost of Insufficient Sleep
Insufficient sleep severely impacts brain function. Cognitive processes such as memory consolidation, learning, and problem-solving skills are adversely affected. Individuals may experience forgetfulness and difficulty retaining information.
There is also evidence linking chronic sleep deprivation to the development of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and dementia. Poor sleep can lead to increased levels of harmful proteins in the brain, potentially accelerating cognitive decline over time. Prioritizing sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal brain health and function.
Practical Tips for Improving Sleep
Improving sleep quality involves establishing effective routines and creating an ideal sleep environment. Attention to light exposure and the management of electronic devices also plays a crucial role in sleep hygiene.
Developing a Bedtime Routine
A consistent bedtime routine helps signal to the body that it’s time to wind down. This routine can include calming activities like reading, meditation, or gentle stretching.
It’s beneficial to go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends. This regularity reinforces the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Limiting stimulating activities in the hour before bed is essential. Engaging in relaxing tasks helps decrease stress and encourages a more restful night’s sleep.
Creating a Conducive Sleep Environment
The sleep environment should be quiet, dark, and cool to promote optimal sleep. The ideal bedroom temperature is typically between 60°F and 67°F (15°C to 19°C).
Reducing noise can be achieved through earplugs, white noise machines, or soundproofing techniques. Limiting exposure to disruptive sounds vastly improves sleep quality.
Blackout curtains and comfortable bedding further enhance the sleeping environment. Creating a space that is inviting and calm can significantly impact the likelihood of restful sleep.
Managing Light and Electronic Devices
Managing light exposure is crucial for regulating the body’s internal clock. Reducing bright light, especially blue light from electronic devices, in the evening helps produce melatonin, the hormone responsible for sleep.
Using apps or settings on devices that reduce blue light emission after sunset can assist in this process. Turning off screens at least an hour before bedtime encourages more natural sleep patterns.
It’s also important to expose oneself to natural light during the day. This exposure reinforces the body’s circadian rhythm and can help improve nighttime sleep quality.
Professional Guidance and Resources
Understanding when to seek professional advice and utilizing reputable resources can significantly enhance sleep quality. Having access to information from trusted organizations can also aid in recognizing sleep disorders and addressing sleep-related issues effectively.
When to Consult a Doctor
Consulting a doctor is essential when sleep disturbances become frequent. Signs that indicate a need for professional help include persistent insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, or noticeable changes in sleep patterns.
Doctors may explore underlying conditions that disrupt sleep, such as sleep apnea, anxiety, or depression. They may also review the patient’s current medications, as some can impact sleep quality.
A thorough evaluation may include sleep studies or referrals to specialists, particularly for complex sleep disorders. Seeking help early can prevent further complications and improve overall health.
Utilizing Sleep Foundation Guidelines
The National Sleep Foundation provides comprehensive guidelines tailored to different age groups. These guidelines suggest the recommended hours of sleep, which vary from newborns needing 14-17 hours to adults requiring 7-9 hours.
Utilizing these guidelines enables individuals to assess their sleep needs against scientifically backed recommendations. They also offer tips on improving sleep hygiene, such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleep environment, and implementing bedtime rituals.
Staying informed about updates from trusted organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) can also provide insights into sleep-related health news and emerging research on sleep disorders.
Click here to purchase the Sleep Diary and start improving your sleep patterns today!*
*There are affiliate links on this page, which means we may earn a small commission should you buy after clicking on one, or more of those links. At no extra cost to you.
Keeping a Sleep Diary: A Useful Tool
A sleep diary is an effective method for individuals to track their sleep habits and identify patterns. It can include information such as sleep duration, time taken to fall asleep, nighttime awakenings, and daily mood.
Recording this data over several weeks reveals trends and assists healthcare providers in making informed recommendations. It can highlight factors affecting sleep quality, such as lifestyle choices or digital device usage before bed.
Moreover, analyzing sleep records can help assess the effectiveness of interventions, including lifestyle changes or medications like melatonin. Ultimately, a sleep diary serves as a practical tool for enhancing individual understanding of personal sleep patterns.
Harnessing Sleep for Overall Well-being
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining health and well-being. It is essential for both physical and mental rejuvenation.
Adequate sleep supports a robust immune system. When the body rests, it can focus on repairing itself and fighting off illnesses.
Quality sleep boosts energy levels. People who sleep well typically feel more refreshed and ready to tackle daily tasks, enhancing their productivity.
A consistent sleep schedule can improve overall mood. Better sleep contributes to emotional stability, which is vital for overall well-being.
Here are some tips for harnessing sleep:
- Establish a Routine: Going to bed and waking up at the same time helps regulate the body’s internal clock.
- Create a Comfortable Environment: A dark, cool, and quiet room promotes better sleep.
- Limit Stimulants: Reducing caffeine and electronics before bed prepares the body for rest.
In addition, good sleep is linked to better cognitive functions. It helps with memory retention and decision-making, leading to a more efficient day.
Incorporating these practices can lead to improved health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life. Adequate sleep is not just a luxury; it is a necessity for sustaining energy and productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Many individuals seek clarity on sleep needs across different ages and circumstances. The following questions address common concerns regarding sleep duration and its effects on health and performance.
What are the expert-recommended sleep durations for different age groups?
Experts recommend varying amounts of sleep depending on age. Newborns typically need 14-17 hours, while toddlers require about 11-14 hours. Teenagers often need 8-10 hours, and adults should aim for 7-9 hours per night.
Can 6 hours of sleep per night be sufficient for optimal health?
For most adults, 6 hours of sleep may not be sufficient for optimal health. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to various health issues, including decreased cognitive function and impaired immune response.
What is the minimum amount of sleep required to maintain proper brain function?
The minimum amount of sleep needed to maintain proper brain function varies by individual. Generally, many adults need at least 6 hours of sleep to function effectively, but 7-9 hours is ideal for cognitive performance.
Are there specific sleep needs for students to support their academic performance?
Students may require more sleep than adults to support their academic performance. Sleep deprivation can affect concentration, memory, and overall learning capacity, making 8-10 hours advisable for school-age children and teenagers.
How does sleep duration influence weight loss in adults?
Insufficient sleep can adversely affect weight loss efforts in adults. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased hunger and a tendency to make poor food choices.
Does the sleep requirement for women change throughout different stages of life?
Yes, sleep requirements for women can change during various life stages. Factors such as pregnancy, menopause, and menstruation can influence sleep patterns and duration, often increasing the need for rest during these times.
MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin Review: Do They Work?

These gummies are designed to promote relaxation and support sleep quality for adults. Unlike many other sleep aids, they don’t contain melatonin, so you won’t wake up feeling groggy or drowsy.
Continue reading: MaryRuth Organics Sleep Gummies Without Melatonin
Reclaiming Deep Restful Sleep: The Magnesium Deficiency Solution

Discover the natural solution to deep, restful sleep and magnesium deficiency through the efficacy of PUREDOSE® Micelle Liposomal Magnesium. This superior bioavailable supplement promotes optimal sleep support and overall well-being.
Continue reading: Reclaiming Deep Restful Sleep
Zarbee’s Kids Melatonin Sleep Gummies for Toddlers*
Are you a parent struggling to get your child to sleep at night? We’ve recently tried out Zarbee’s Kids 1mg Melatonin Sleep Gummies for toddlers, and we’re impressed with the results.
One of the best features of Zarbee’s Kids 1mg Melatonin Gummy* is that it’s pediatrician-approved. The brand was developed by a father and pediatrician, Dr. Zak Zarbock, and has become the #1 Pediatrician Recommended Sleep Support Brand for Children.
*As an Amazon.com Affiliate, we may earn a small commission if you buy from a link within this page.







