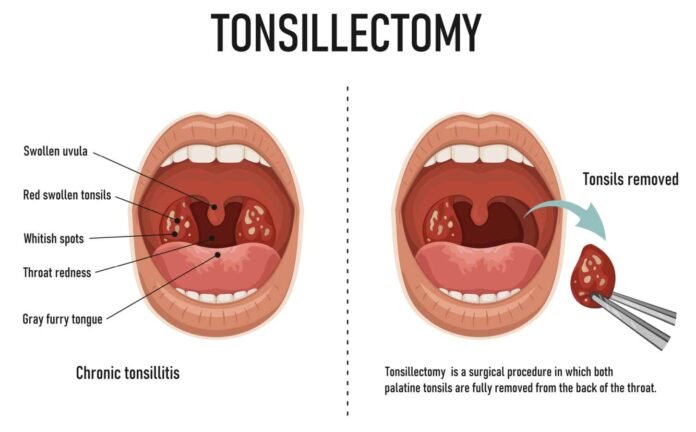
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tonsils.
The tonsils are two small glands located at the back of the throat, which play a role in the immune system. They can become infected and inflamed, leading to conditions such as tonsillitis, sleep apnea, or difficulty swallowing. In some cases, a tonsillectomy may be recommended to alleviate these symptoms.
During the procedure, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, and the tonsils are removed through the mouth. The surgery typically takes about 30 minutes to an hour, and patients are usually able to go home the same day. Recovery time can vary, but most patients can return to normal activities within two weeks.
While a tonsillectomy is a relatively safe and common procedure, it is not without risks. Complications can include bleeding, infection, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. It is important for patients to discuss the benefits and risks of the procedure with their healthcare provider to determine if a tonsillectomy is the right choice for them.
Understanding Tonsillectomy
Definition and Purpose
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the tonsils. The tonsils are two small glands located at the back of the throat. They are part of the immune system and help to fight off infections. Tonsillectomy is usually performed to treat recurrent tonsillitis, sleep apnea, or other conditions that affect the tonsils.
The purpose of tonsillectomy is to relieve symptoms and improve the overall health of the patient. The surgery is usually performed on an outpatient basis and can be done under local or general anesthesia.
Anatomy of Tonsils
The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system and are made up of three types of tissue: palatine tonsils, adenoids, and lingual tonsils. The palatine tonsils are the most commonly removed during tonsillectomy. They are located on either side of the back of the throat and are visible through the mouth.
The adenoids are located at the back of the nasal cavity and are not visible. They are often removed along with the tonsils if they are causing problems.
The lingual tonsils are located at the base of the tongue and are not usually removed during tonsillectomy.
Indications for Surgery
Tonsillectomy may be recommended for a variety of reasons, including:
- Recurrent tonsillitis: If a patient has frequent episodes of tonsillitis that do not respond to other treatments, tonsillectomy may be recommended.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: Tonsillectomy may be recommended if a patient has sleep apnea caused by enlarged tonsils.
- Other conditions: Tonsillectomy may also be recommended for other conditions, such as periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, or adenitis.
Tonsillectomy is generally considered safe and effective for treating these conditions. However, as with any surgery, there are risks involved. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with their healthcare provider before deciding to have the surgery.
Adenoidectomy: Procedure, Recovery, and Risks
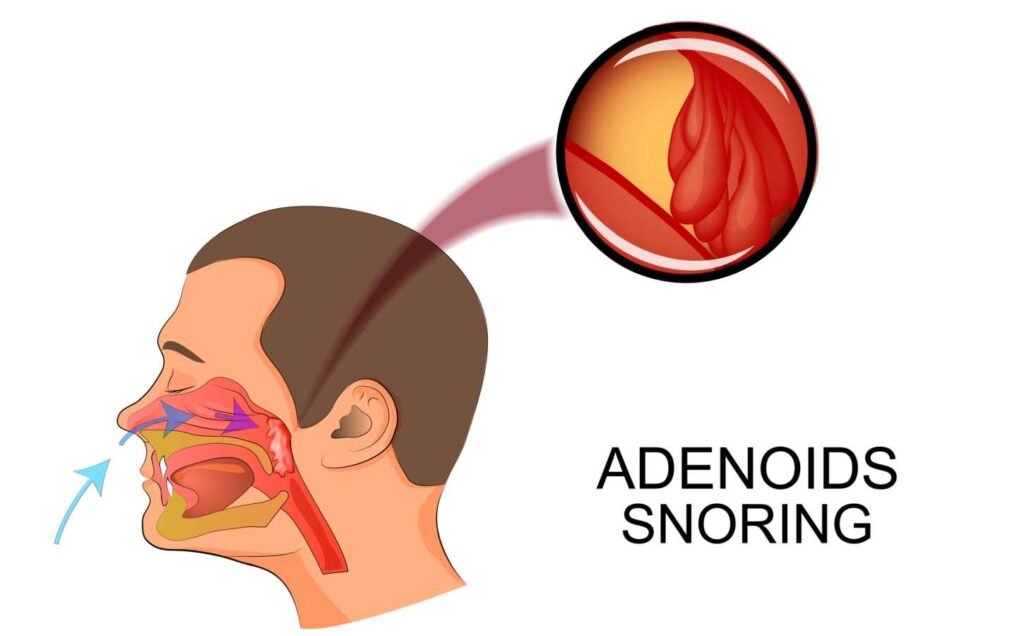
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed by an otolaryngologist to remove the adenoids, which are small glands located at the back of the nasal cavity.
Adenoids are small glands located at the back of the nose, just above the tonsils. They are part of the immune system and help to fight off infections that enter the body through the nose. Adenoids are most active during childhood and tend to shrink in size as a person grows older.
Continue reading: Adenoidectomy: Procedure, Recovery, and Risks